HTML
-
光纤激光器具有结构简单、光电转换效率高、光束质量好和热管理方便等显著优点,在工业和国防领域有广泛的应用前景[1-4]。但由于受介质非线性效应、热透镜效应、光纤端面损伤及热损伤等因素的影响[5-6],单台光纤激光器输出功率存在受限,并且光束质量随着输出功率的增大而降低。为了获得高功率高质量的输出光束,可通过构建光纤激光阵列,采用光束合成的方法将多路光束合并为一束[7-9]。根据参与合成的各路单元光束间的相干关系,光束合成分为非相干合成和相干合成。受到受激布里渊散射(stimulated Bri-llouin scattering,SBS)的限制,用于相干合成的窄线宽线偏振光纤激光最大输出功率仅在千瓦量级[10]。非相干合成对单元光束的相位、谱宽和偏振态等没有特殊要求,目前单模宽谱光纤激光器输出功率已达到万瓦级[11]。这意味着要获得相同的输出功率,非相干合成系统所需单元数远远少于相干合成,大大减小了系统的复杂性。高能激光对目标的作用效果不仅取决于激光器总输出功率,与激光光束质量也有着密切关系。
本文中从合成光束质量的角度出发,以远场光束质量β因子作为评价标准,针对光纤激光阵列圆环状排布的情况,对不同单元光束束腰半径、波前畸变和光束间距情况下的非相干及相干合成远场光束质量进行了数值模拟计算。并且,对不同多路激光平行性下的非相干合成结果进行了讨论分析,并进行了相关实验验证。
-
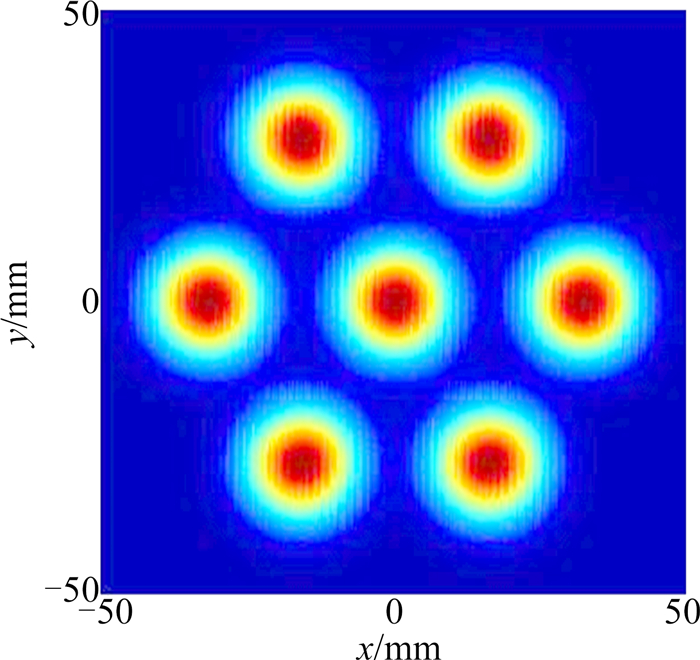
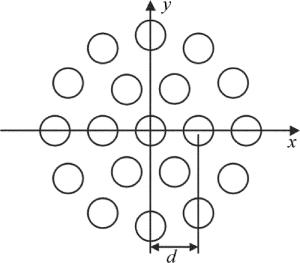
对于光纤激光器,输出光束截面为圆形,假设多路光纤激光在近场按图 1所示的圆环状分布排列,单元光束束腰半径为w0,相邻单元光束中心间距为d。若中心路单元光束外有N圈阵列光束,则激光阵列总单元数M=3N(N+1)+1。在该模型中,单元光束中心间距d越小,表明单元光束之间的距离越小,激光阵列排布越紧凑。特别地,当单元光束中心间距d=0时,光束合成由分孔径合成变为共孔径合成。
假定单元光束服从高斯分布,光束束腰位于z=0的平面上,传输距离z处的光场分布为[12]:
式中,k为波数,且k=2π/λ,λ为激光波长;Φq为附加相位因子, (xq, yq)为第q路单元光束的中心坐标,q为整数。圈数N=1,总单元数M=7的激光阵列:对于中心路单元光束,x0=y0=0;对于圆周单元光束,xq>=dcos(π/3×q),yq=dsin(π/3×q),其中,q=1,2,…,6。图 2即为一典型光纤激光阵列光束的近场光强分布,本文中主要对这种情形进行模拟分析。
高功率光纤激光器受热透镜效应等因素的影响,输出光束或多或少存在一定程度的波前畸变,波前畸变相位可以采用随机相位屏的方法进行构建[13-14]:
式中,A为低频相位幅度,R(-1, 1)为-1~1均匀分布的2维随机数序列,⊗为卷积运算符,gx和gy为x、y方向上的相位畸变起伏参量,σ为高频扰动幅度。
根据广义惠更斯-菲涅耳衍射积分公式,单元光束远场分布可以表示为:
式中,f为聚焦系统的焦距,d1为激光器输出到聚焦系统的距离。
对于非相干合成,合成光束的远场光强分布为:
相干合成光束的远场光强分布为:
-
光束合成效果可以以远场光束质量β因子作为评价标准。光束质量β因子定义为被测实际光束远场发散角θr与同样尺度的理想光束远场发散角θi之比。对于高斯光束,其理想远场发散角θi为[15]:
式中,D为聚焦系统有效通光孔径直径。
实际光束远场发散角θr由光束发射系统聚焦后远场光斑环围功率半径r与焦距f的比值计算得到。环围功率半径r是根据规范功率份额定义的,即以远场光斑的质心为中心,包含规范功率份额P0的桶半径[16]。对于高斯光束,规范功率份额P0=86.5%。
1.1. 激光阵列光束理论模型
1.2. 评价参量
-
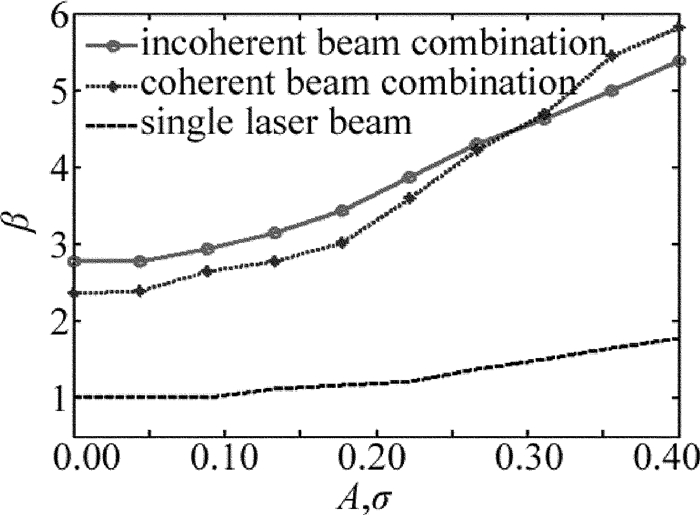
对于不同束腰半径w0的单元光束组成的激光阵列光束,图 3中给出了单元光束有无波前相位畸变的非相干及相干合成远场光束质量β因子随光束间距d的变化。图中,波前相位畸变Φ=0即为单元光束波前相位无畸变,Φ≠0对应单元光束波前存在畸变:低频相位幅度A=0.23,相位畸变起伏参量gx=gy=0.05,高频扰动幅度σ=1.0。图 3a中单元光束束腰半径w0=10mm,图 3b中单元光束束腰半径w0=13mm。当光束中心间距d=0mm时,非相干及相干合成光束质量与单元光束的光束质量一样。
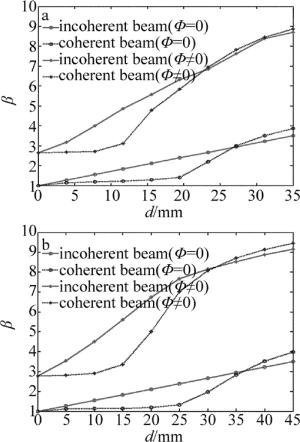
Figure 3. Variations of beam quality of incoherent and coherent beam combination with beam separation distance a—w0=10mm b—w0=13mm
从图 3中可以看出,对于不同束腰半径w0单元光束组成的激光阵列,非相干及相干合成光束质量β因子随光束中心间距d的变化趋势是相似的。当光束间距d较小,各路单元光束间重叠较多时,相对于非相干合成,相干合成光束质量更好;随着光束间距d的增大,非相干及相干合成光束质量都逐渐变差,当光束间距d增大到一定时(这里假设非相干和相干合成光束质量β因子相等时的光束间距为d0,经多组数值模拟计算发现,单元光束波前相位无畸变时,d0/w0=2.8),非相干合成光束质量更好。单元光束存在波前畸变时,非相干及相干合成光束质量都有所变差。值得注意的是,相较于单元光束无波前畸变,单元光束波前发生畸变时d0/w0比值有所减小。
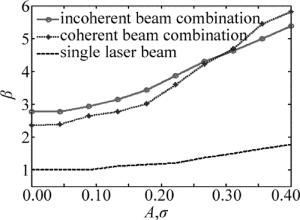
为了进一步明确单元光束波前畸变对非相干及相干合成效果的影响,图 4中给出了单元光束波前畸变程度不同情况下的单路、多路非相干及相干合成远场光束质量(相位畸变起伏参量gx=gy=0.05)。在实际光纤激光光束合成系统中,受聚焦发射望远镜系统设计和机械装配等因素的影响,各路光束排布不可能无限紧密。这里取单元光束束腰半径w0=13mm,光束中心间距d=32mm。
从图 4可以看到,随着低频相位幅度A和高频扰动幅度σ的增大,即单元光束波前畸变程度的增大,单路、多路非相干及相干合成光束质量β因子均逐渐增大。并且,当单元光束波前畸变程度较小时,相较于非相干合成,相干合成光束质量更好;但是当波前相位畸变增大到一定程度时,非相干合成效果更好,这是因为相比于非相干合成,相干合成过程中还反映了多光束彼此之间的干涉效应,波前畸变程度的变化在相干合成中体现更多,对其合成效果影响更大。
-
为了得到较好的光束合成效果,光束合成装置需要将多路激光光轴相互调平行。定义各路光束光轴与中心路光束光轴的不平行度为θq,q=1, 2, …, 6。这里为了便于计算讨论,假设每路激光光轴与中心路光轴的不平行度均为θ。当各路激光光轴与中心路光轴不平行度θ分别为0μrad, 5μrad, 10μrad, 15μrad, 20μrad, 25μrad时,激光阵列非相干合成远场光斑分布如图 5所示,并将计算得到的非相干合成远场发散角及光束质量β因子填入表 1。当单元光束波前畸变参量gx=gy=0.05,A=0.23,σ=1.0时,单路远场发散角为0.106mrad,光束质量β因子为2.782;当gx=gy=0.05,A=0.20,σ=0.9时,单路远场发散角为0.083mrad,光束质量β值为2.168。
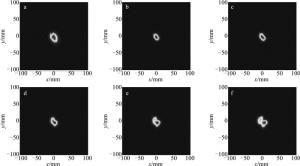
Figure 5. Far-field intensity distribution of incoherent beam combination at different parallel errors (A=0.23, σ=1)
parallel error θ /μrad wave-front distortion(A=0.23, σ=1.0) wave-front distortion(A=0.20, σ=0.9) divergence angle/mrad β divergence angle/mrad β 0 0.114 8.295 0.086 6.250 5 0.114 8.295 0.091 6.590 10 0.122 8.863 0.098 7.159 15 0.125 9.090 0.102 7.386 20 0.130 9.431 0.109 7.954 25 0.138 9.999 0.117 8.522 Table 1. Far-field divergence angle and beam quality of incoherent beam combination at different parallel errors
从图 5和表 1可以看出,随着各路激光光轴与中心路光轴不平行度θ的增大,非相干合成远场能量集中度逐渐降低,远场发散角及光束质量β因子存在不断增大的趋势,非相干合成效果越来越差。这是因为对于非相干合成来说,多路激光之间的不平行主要体现在各路单元光束在远场的偏移。并且可以发现,为了获得较好的非相干合成效果,所期望各路激光的光束质量越好,那么对多路激光之间的平行性要求就越高。
-
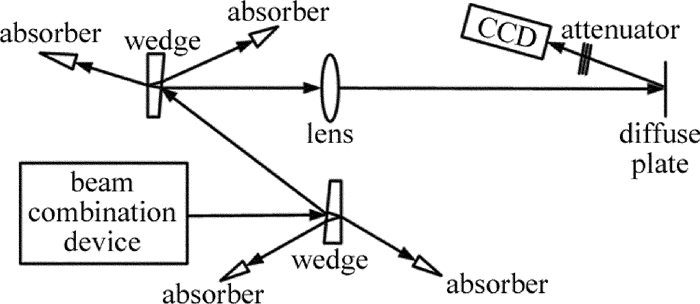
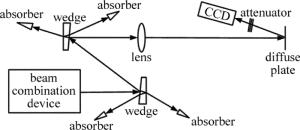
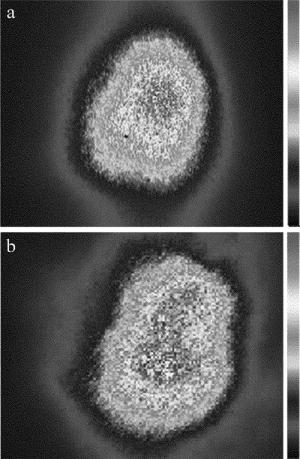
7路激光经光束合成装置调平行后,从同一光学口径输出,经石英光楔分光衰减后,再经透镜聚焦在均匀漫反射屏上,光楔透射和反射的无用光束用激光吸收体吸收,实验系统原理图如图 6所示。实验中,7路激光经光束合成装置后最大不平行度分别小于5μrad和10μrad时,CCD采集到的光斑图像如图 7所示。同时,表 2中给出了根据采集到的远场光强分布计算得到的远场发散角及光束质量β因子,以及采用同种排布方式的7路阵列光束模拟计算结果。计算所用参量:单元光束束腰半径w0=13mm,光束中心间距d=32mm,单元光束远场发散角在0.11mrad~0.13mrad。
parallel error θ /μrad experimental results simulated results divergence angle/mrad β divergence angle/mrad β 5 0.120 8.727 0.118 8.636 10 0.128 9.308 0.126 9.147 Table 2. Far-field divergence angle and beam quality of incoherent beam combination
从图 7和表 2可以看到,随着多路激光最大不平行度从5μrad增大到10μrad,非相干合成远场能量集中度明显降低,非相干合成远场发散角及光束质量β因子值均有所增大,并且,实验结果与模拟计算结果较为一致。
3.1. 多路激光平行性对非相干合成效果的影响
3.2. 实验验证
-
本文中通过建立圆环状排布的光纤激光阵列光束合成模型,模拟计算了不同单元光束束腰半径、波前畸变和光束间距下的非相干及相干合成远场光束质量。结果表明:对于同一束腰半径w0的阵列光束,随着光束中心间距d的增大,非相干及相干合成光束质量都逐渐变差,当间距d>d0时(单元光束无波前畸变时,d0=2.8w0;单元光束存在波前畸变时,d0有所减小),非相干合成光束质量更好。随着单元光束波前畸变程度的增大,非相干及相干合成光束质量逐渐变差,当波前相位畸变增大到一定程度时,非相干合成效果更好,这是因为单元光束波前畸变对相干合成的影响更大。此外,详细讨论了多路激光平行性对非相干合成效果的影响,并进行了相关实验验证。随着多路激光之间不平行度的增大,非相干合成远场能量集中度逐渐降低,非相干合成效果越来越差。为了获得较好的非相干合成效果,期望各路激光的光束质量越好,那么对多路激光之间的平行性要求就越高。

 Map
Map





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: