HTML
-
1998年,EBBESEN等人[1]通过实验发现,当一束平行光照射具有亚波长小孔阵列结构的金属薄膜时,透射光能量与入射光能量的比值比传统衍射理论的估计值提高了4个数量级,归一化透过率的值超过2。由于这种增强效应突破了经典理论的限制,在平板显示器、微腔量子电动力学、滤波器等无源纳米器件设计及近场光学等领域具有巨大的应用潜力[2-9]。众多研究者[10-12]对其物理机理进行了研究,发现表面等离子体激元在其中起到了重要作用,它是入射光与金属表面自由电子的电荷密度波发生共振耦合作用而形成的局域近场增强,能极大地提高光的透射效率。
本文中以玻璃衬底上亚波长的金属纳米柱阵列结构为研究对象,采用时域有限差分法[13-15]求解特定边界条件下的麦克斯韦方程组来模拟研究光通过亚波长金属柱阵列膜的透射增强特性。研究发现,金属纳米柱阵列也具有很好的超强透射特性。研究了不同的阵列周期、不同的金属柱高度及不同金属材料的增强光透射谱的带通特性,提出了该柱阵列金属膜结构在光带通滤波微器件设计中的应用。
-
图 1是玻璃衬底上的金属柱阵列的结构模型,玻璃衬底上方除金属柱外均为空气介质(介质常数ε=1),金属柱采用紧凑对称排列,如图 2所示。光源沿z轴方向由玻璃衬底中竖直向上入射,偏振方向沿x轴方向,入射光源为平面波,波长为800nm~2400nm。考虑所研究光频段金属的色散特性,采用Drude模型[16]来表述金属材料的介电常数与光频率ω的关系:
式中, ωp为等离子体频率;γ为电子的碰撞频率; ε∞为频率很大时金属的介电常数。
该模型在600nm~2400nm可以描述金属介电特性,其色散模型拟合参量如下所示[17]。Ag:ε∞=3.5790,ωp =1.3873×1016rad/s, γ=3.2044×1013rad/s; Au:ε∞=4.8952,ωp=1.3361×1016rad/s, γ=1.2315×1014rad/s。本模型选取的边界条件为:x方向是反对称边界条件,y方向是对称边界条件,z方向设为完全匹配层边界条件。作者采用3维时域有限差分方法计算光束透射过金属膜的电场、磁场分布,由时域场量的傅里叶变换而得到透射光谱。归一化透过率[18]定义为:
式中, T为透过率;Sgap为单元面积上空隙的面积; Scell是单元面积;Sgap/Scell为占空比。
-
本文中就上述紧凑型金属柱阵列结构模型和条件进行了计算,得到了不同金属材料、不同金属柱半径和高度情况下的光透射增强谱,并对光谱的特性随计算参量的变化情况进行了分析。
-
设定银柱的高度80nm不变,选取平面波光源的波长范围为800nm~2400nm。计算不同银柱半径(相应于不同银柱阵列周期)情况下的透射光谱,银柱半径r为200nm~380nm,选取8个点进行计算,得到的透射率如图 3所示。在很宽的光谱范围内透射谱呈主带结构。透射谱峰值波长在800nm~1600nm之间变化,其透射带的半峰全宽(full width at half maximum, FWHM)由220nm增加到380nm。在较宽的金属柱半径变化范围内,峰值透过率超过0.9, 可求得相应的归一化透过率为4.19,此时的归一化透过率远超过1。光超强透射现象与表面等离子体激元有紧密联系,由于表面等离子体激元的激发,导致增强的电磁场,在金属表面区域产生局部电磁场比入射光场有一定程度的增强。
-
为分析银柱高度对透射增强效应的影响,固定银柱阵列周期不变,即半径不变。使用的平面波光源的波长范围为1000nm~2200nm。计算不同银柱高度情况下的透射谱,在银柱高度h为30nm~130nm的变化范围内选取8个点进行计算,得到的透射谱结果如图 4所示。可以看出,在银柱高度h为30nm~60nm时,随着h增加,透射率增加,约在h=60nm时,峰值透射率达到最大。之后随着高度h增加,峰值透射率逐渐下降,其变化关系如图 5所示。这是因为在金属的上下界面上传播的波通过小孔相互耦合的效率和金属薄膜的厚度息息相关的,金属薄膜越薄,这种耦合作用越强[12]。随着银柱高度的减小,倏逝波能够将更多的能量转移到薄膜的上表面。在h=60nm时,峰值透过率超过0.977, 可求得相应的归一化透过率为4.55,这是由于表面等离子体效应而产生超强透射现象。
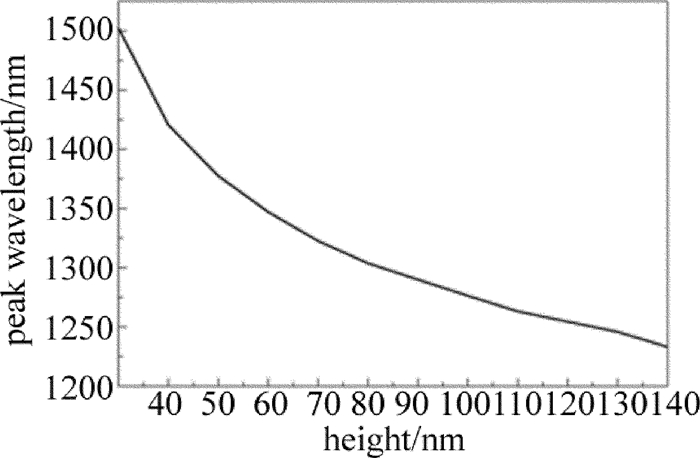
结果还表明,当膜厚为30nm时,其透射带的峰值波长为1500nm,FWHM约为575nm,随膜厚度的增加,峰值位置不断减小到1250nm,FWHM也单调减小210nm,如图 6、图 7所示。
-
上面已经主要分析了银柱阵列参量的改变对透射谱的影响,下面将银柱的材料换为金,在相同模型下进行透射谱的计算并与前面银材料进行对比。
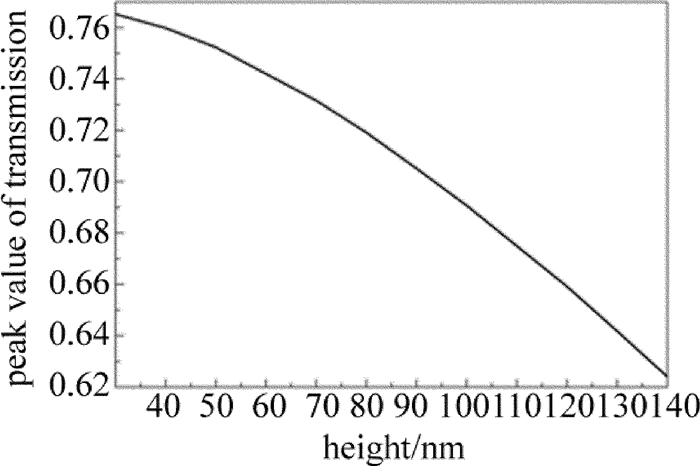
固定金柱阵列周期不变,即半径不变。金属柱高度的变化范围h为30nm~130nm,选取8个点进行计算,平面波光源的波长范围为800nm~2000nm。计算得到的透射谱结果如图 8所示。可以看出,随着金柱高度增加,透射带的峰值波长从1300nm减小到1000nm,透射带的半峰全宽也单调减小,而透射带的峰值透过率由0.76单调减小为0.63,如图 9所示。这与银材料的透射率的大小与变化情况不同。而固定金柱高度不变,对透射谱随金柱半径变化的情况也进行了计算,结果显示,随着金柱半径的增加,透射谱峰值先增加后趋于平稳,透射带的半峰全宽逐渐减小,透射率峰的波长位置不断增大,这些除透过率较小外与银材料的相似。
2.1. 银柱底面半径对透射谱的影响
2.2. 银柱高度对透射谱的影响
2.3. 金柱阵列对透射谱的影响
-
采用时域有限差分法研究了光通过玻璃衬底上的亚波长金属柱阵列的传输特性。结果表明,不同的亚波长金属柱阵列周期和金属柱高度均具有带通透射特性,且在特定的波长范围内会出现超强透射增强现象,归一化的透射率可达到4.5以上。对金和银两种金属的模型进行了优化计算和分析,结果表明,银膜的峰值透过率超过0.9, 通过改变阵列周期可使峰值波长在800nm~1600nm之间变化,其透射带的半峰全宽也由220nm增加到380nm。研究结果为光带通滤波微器件的设计提供了一种新的方案,且滤波通带中心波长和通带带宽可通过调节金属柱阵列周期和金属膜厚度在很宽的范围内进行选择。

 Map
Map













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: