HTML
-
激光多普勒测速仪(laser Doppler velocimetry, LDV)系统具有测量精度高、非接触测量、动态响应迅速以及测量量程大且抗外界环境干扰能力强、能够测量1-D, 2-D, 3-D及多维速度[1]、还可以判断速度的运动方向等诸多优点[2]。LDV系统利用激光多普勒效应产生的频移和速度的线性关系,通过测量多普勒频移计算出固体运动的运动速度,为轧钢生产速度提供精确的速度参量,这对生产高质量的轧制产品都具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。LDV系统中速度信号修正是LDV测速的关键环节,目前,多普勒信号处理的最常见的方法有快速傅里叶变换(fast Fourier transformation, FFT)、小波分析法。FFT方法具有很强的从噪声中提取信号的能力且可以接收间断信号的优点,但用FFT结果的峰值谱对应的频率作为多普勒频率值,则存在测量精度低的问题,不能满足多普勒测速的要求。又因为LDV测量范围和实时测量的要求,对信号的采样频率和信号的长度做出改变来提高频率分辨力不太现实,因此,介于激光多普勒测速信号中夹杂的一系列干扰噪声,通过小波特性的分析,选择将高频系数部分置零的滤波方法进行滤波[3],最终使信号的高频部分和低频部分都得到了理想的恢复。本文中的研究证明了此方法在激光多普勒测速系统中信号处理的准确及有效性。
-
假设一个信号f,将其作为原信号,那么将f正交小波分解,分解的公式为:
式中, k=1, 2, 3, …, n-1;aj(n)为近似系数; dj(n)为细节系数; 表示低通滤波函数; g为高通滤波函数; j为分解层数; n为采样的点数。信号aj(n)经过网络的特性为h(n)的低通滤波器,再选取偶数样本然后获得aj+1(n),信号aj(n)经过高通滤波器g(n),之后再选取偶数样本就可获得dj+1(n)。
小波重构[4]表达式为:
对于一些平稳的信号,能量大都在低频系数里,仅有较少的细节重叠在高频系数里,对含噪信号来说,大都在高频系数里[5]。对于非平稳信号来说,其能量分布在所有频域,由此来看,其信号和噪声的频域会产生重叠[6]。由上可知, 小波变换就是将信号利用低通、高通两组滤波器,分解为高频系数和低频系数。利用线性小波分析[7]的方法,通过选取合适的小波基,将信号与噪声重叠的部分尽可能减小。小波分析的一个应用方面就是选择小波分析对信号滤波[8]。
-
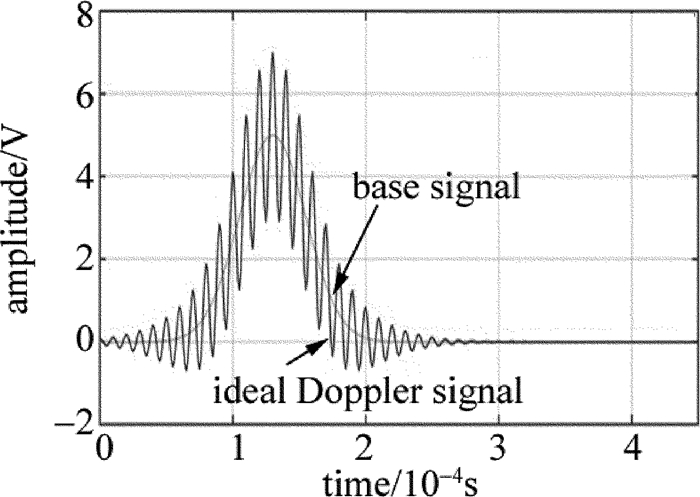
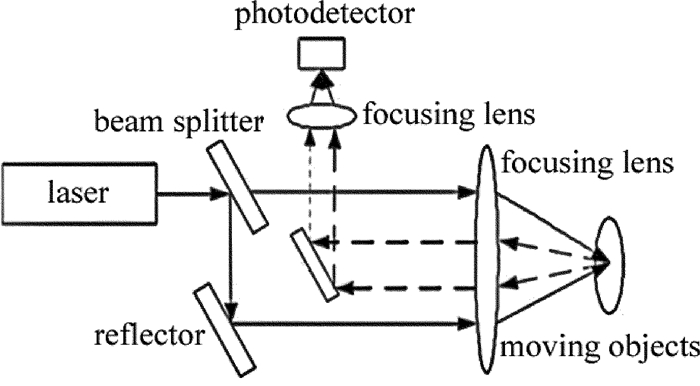
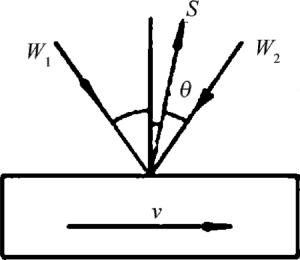
1968年,RUDD在利用激光器测量散射运动粒子的运动速度时,发现多普勒频移会引起激光强度波动。参考文献中运用干涉条纹模型阐述了差动多普勒信号。LDV的原理就是采用此方法进行测速的,而且以其可测体积小、响应速度快、测量精度高、测量量程大、可多维测量和非接触测量等被广泛地应用于工业领域[10]。在搭建的实验系统中,光路模式运用双光束-双散射模式光路[11],这是因为仅有两入射光方向对多普勒频移产生影响[12]。在实际中,W1和W2两光束入射到运动物体的外表层,在被测物体外表层出现极小的检测光斑,两入射光束都将被散射,考察S方向上的散射光频移,如图 1所示。
多普勒频移与速率的关系如下:
式中,Δf为多普勒频移; θ为入射光线与交角平分线的夹角; λ为光波波长。采用条纹模型[13]便于阐述系统检测信号的特征。激光属于高斯光束,因此激光符合高斯光束的特性,即中间光强强度高,向四周辐射逐渐变弱[14]。在实验测速系统中,由光源发出的光会被光学元件均分为1:1的两束入射光[15](这里的光源为He-Ne激光器),恰好两束入射光束在空间上彼此重叠一部分,形成条纹模型,倘若有一个正以速率v穿过测量体的运动粒子,则光路系统中的光电检测器就会采集到一个电流信号,其信号表达式i(t)[16]为:
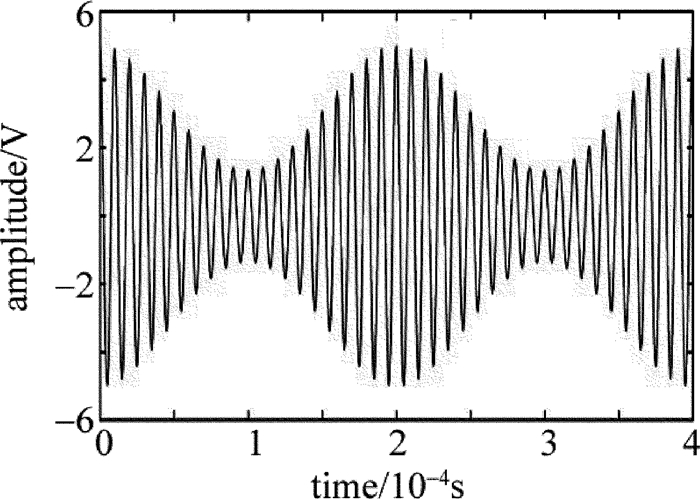
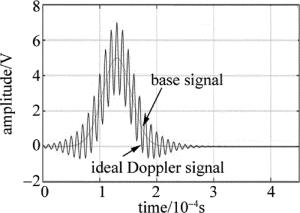
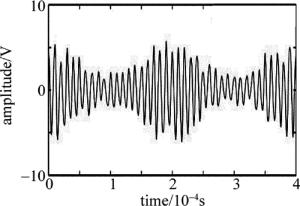
由(4)式可以发现,信号主要由两部分组成:一是频率较低的基底,幅度为id; 另一个是余弦窗(图 2中理想多普勒信号),幅度为ia,这部分信号是重叠在基底上的,主要工作就是对此信号进行处理[17]。在这里设id=5,ia=2,t=1/Fs, Fs为采样频率,t0=a/Fs为粒子到达的时间,信号a=a1,a2,…,a20, 且a1=0;τ=Nf/FD, τ为运动粒子穿过控制体用的时间,Nf为条纹数目,FD为多普勒频移。构造的仿真信号就是i(t)=i1+i2+i3+i4,仿真信号由多个基波信号构成,倘若信号a=a1, an+1-an=120时,则i(t)=i1, i1为一个基波信号。图 2为理想信号时域波形图。
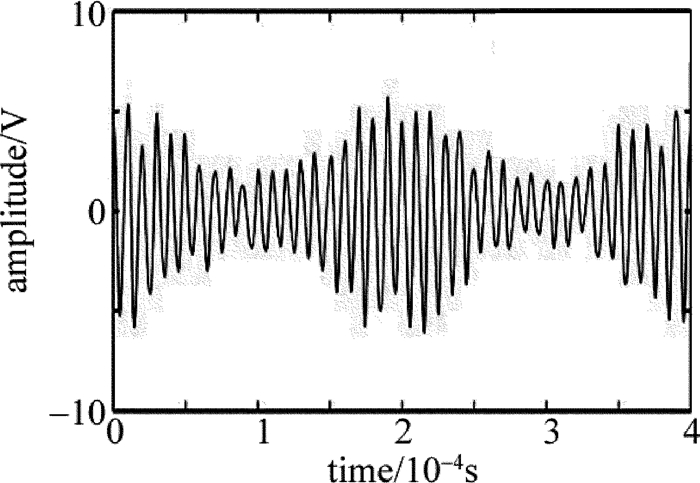
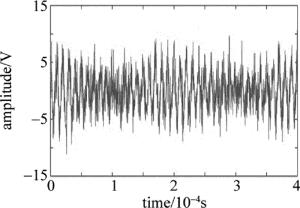
下面假设an+1-an=1000时,进行信号构造。图 3为4个基波信号进行构造生成并经基底滤波后得到的不加噪声的原仿真信号。图 4为加噪仿真信号波形。
-
为了便于比较高频系数置零去噪效果,本文中对含噪激光多普勒测速仿真信号采用高频系数置零和小波阈值去噪两种去噪方法。
-
原理如下:首先对加入噪声的仿真信号进行层数分解,干扰信号[18]大都在高频系数里面,然后把高频系数部分的系数置零,最后对修正过的信号重构,恢复后产生的新信号就为滤波之后的信号[19]。去噪方法基本步骤如下:(1)基于带有噪声的多普勒测速信号,选取合适的基函数以及需要的层数,对带有噪声的多普勒测速信号处理后来获得每一层的分解系数; (2)将每层所得的高频系数置零; (3)再将步骤(2)置零后的系数和对应层的低频系数进行重新构造,获得的信号就是最优系数重新构造后的信号。
-
对信号进行小波分解,分解的层数越多其产生的子带越多、频带也划分的越细,但同时也会造成信号位移增大、边界失真严重。因此,分解层数的选取并不是越大越好,选择合适的分解层数也是影响测速精度的关键因素之一。分解层数确定流程如下:(1)分解层数j; (2)信号小波分解; (3)分解系数处理; (4)信号重构; (5)结果评估; (6)确定最优; (7)分解层数。
分解层数j取1层~6层,如表 1所示。
j 1 2 3 4 5 6 SNR 3.15 6.29 8.75 11.89 0.15 -0.07 Table 1. Comparison of decomposition layers 1 to 6
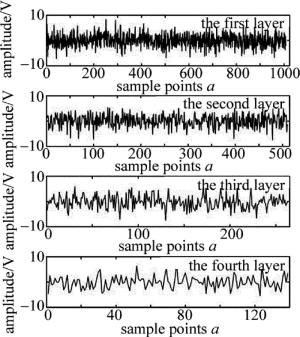
从表 1中可以看出, 分解层数由1层~4层时,信噪比呈上升趋势,到达4层时, 信噪比(signal-to-noise ratio, SNR)达到峰值,取到5层时信噪比出现巨大拐点,甚至取到6层时信噪比呈现为负值。鉴于基函数与实验信号的特征类似,特征愈相近,小波变换后的信号与干扰信号的频带重叠区域就会愈小,去噪的效果也就会更优越。鉴于sym8基的优越性,本次选取sym8基,层数选取为4层,分解后各层分量如图 5和图 6所示。
近似分量为图 5,细节分量为图 6。分别将图 6每层分量置零,将系数置零处理后即可进入下一步。再对系数采用小波重构,如图 7所示。最后重构修正后获得最优小波系数。
-
阈值选取规则,目前常用的4种阈值规则heursure, sqtwolog, rigrsure, minimaxi阈值规则[20],本次将sym8小波作为滤波小波基,分别对仿真信号4层分解,同时对信号小波阈值去噪。小波阈值去噪结果如图 8所示。
-
区别不同滤波方法的滤波效果,这里应拟定一个标准来作为滤波效果优良的依据。常用的评价信号去噪效果的参量如下。信噪比RSNR见下式:
式中, Ps为原始信号的功率; Pn为白噪声的功率。去噪效果好坏与信噪比成正比关系,因此要获得较大信噪比,来达到更好的效果[21]。均方根误差(root mean square error, RMSE)见下式:
式中,x(n)为原始信号; xs(n)为滤波信号; N为信号的长度。ERMSE越小, 说明去噪的效果越好。去噪效果比较见表 2。对比观察发现,本次选取的滤波方法对仿真信号滤波后的效果是较为理想的。
analytical method this article heursure rule sqtwolog rule rigrsurerule minimaxi rule SNR 11.89 11.25 11.22 9.99 11.11 RMSE 0.40 0.43 0.45 0.56 0.48 Table 2. Comparison of denoising effects
2.1. 信号仿真
2.2. 仿真信号去噪分析
2.2.1. 高频系数置零去噪方法
2.2.2. 小波分解层数确定
2.2.3. 小波阈值去噪
2.3. 去噪效果评价参量
-
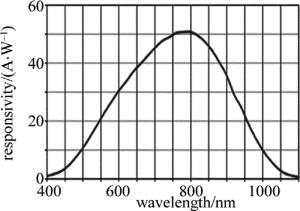
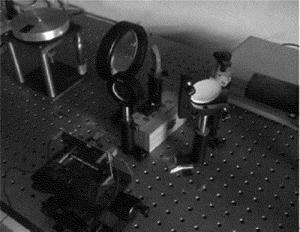
此次实验光学系统-后向双光束-双散射系统如图 9所示。在搭建的实验测速系统中,通过使用电动机带动铝盘转动来模拟带材的运动,采用光电编码盘获得铝盘实际转速; 光源选为偏振光He-Ne激光器,其波长为632.8nm,功率为2MW; 光电探测器[22]型号选择德国First Sensor公司的HSAD230-8-LCC6.1贴片雪崩光电二极管(avalanche photodiode, APD),暗电流为0.3nA,增益为102~103,上升时间为0.18ns,噪声等效功率为10W~15W,响应频率为2GHz,APD光谱响应图如图 10所示,光学系统实物如图 11所示。
通过实验室搭建的LDV系统实验平台,对采样频率为1MHz,5种不同速率的铝盘进行实验。利用光电编码盘测得铝盘的实际转速, 并通过计算得到实际的多普勒频移, 如表 3所示。
number of groups velocity/(m·s-1) frequency shift/Hz 1 2.0420352 1431742.8 2 1.0810774 757981.5 3 0.7689672 539150.0 4 0.4786020 335564.7 5 0.3995286 280123.6 Table 3. Calibration speed and frequency shift
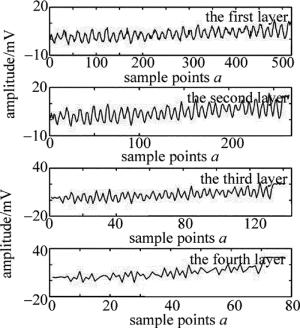
任选速率为0.4786020m/s的实验数据为例实施实验并进行数据采集,从中截取一组数据,从获得的数据中随机截取1024个采样点,将1024个点分解,分解层数为4层,截取的实验信号如图 12所示,分解后生成的近似分量如图 13所示,细节分量如图 14所示。
利用对高频系数置零的去噪方法对激光多普勒测速信号进行去噪,对处理过后的实验信号小波分解的近似分量与细节分量进行小波重构,重构后的实验信号去噪结果如图 15所示。
在目前常用的4种阈值规则,即heursure, sqtwolog, rigrsure, minimaxi阈值规则下进行阈值去噪,效果如图 16所示。
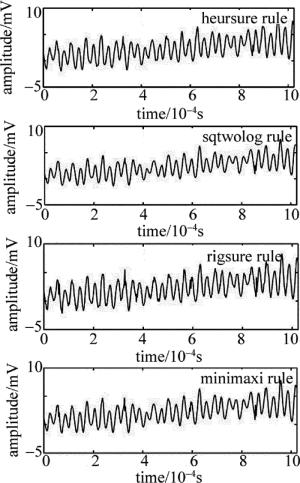
Figure 16. Experimental signal denoising with four methods of heursure, sqtwolog, rigrsure, minimaxi
实验最终目的是测量质量较好的测速参量,对实验数据消噪后不同实验方法测量结果如表 4所示。
experimental method frequency shift/Hz velocity/(m·s-1) rated parameters 335564.7 0.4786020 this article 332031.2 0.4735623 heursure rule 312171.9 0.4453395 sqtwolog rule 305499.2 0.4358203 rigrsure rule 317026.3 0.4522647 minimaxi rule 315280.6 0.4497743 Table 4. Results of frequency shift and speed measurement
-
基于激光多普勒测速信号中所含噪声,提出了小波分解后对高频部分的系数置零去噪的方法对噪声小波系数进行修正。在仿真激光多普勒测速信号中加入高斯白噪,然后通过高频系数置零和小波阈值去噪2种方法进行仿真去噪,并进行实验对比分析,其仿真及实验结果表明, 小波分层去噪法对激光多普勒测速信号进行去噪能够提高信噪比,能够获得图形光滑的理想信号,去噪效果较佳,可进一步提高在激光多普勒测速系统信号检测应用中的准确性。

 Map
Map

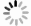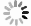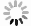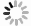








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: