HTML
-
电力线快速提取和重建是基于激光点云输电线路运检的核心技术之一[1-9],大批科研人员参与到研究当中。MELZER和BRIESE最早提出电力线投影到2-D平面,然后应用霍夫变换识别、提取电力线点云[1, 10];参考文献[11]中基于三角网加密滤波、首次回波信息分离地面、高低植被、电力线,最后采用双曲余弦函数完成电力线建模;参考文献[12]~参考文献[14]中采用针对地形起伏的机载LiDAR点云滤波方法,分割掉大部分非电力线点云,然后采用霍夫变换检测电力线; 参考文献[15]中采用一种基于模型增长的电力线提取方法,首先将原始点云数据网格化为多个体素,然后运用Hough变换、主成分分析、密度分析等方法识别其中的电力线点云,最后运用悬链线方程拟合电力线点云。
上述激光点云提取电力线方法虽然取得了一定的成果,但进一步分析发现,这些研究依然存在一些不足。首先这些研究未考虑剔除交跨线、绝缘子点云,这会直接影响电力线重建和隐患分析的效果;其次对电力线模型研究不充分,没有充分开展对电力线在x-O-y平面投影重合模型的研究,大大降低了算法适用范围;此外,上述研究对于算法效率的考虑有所欠缺,算法耗时长,无法适应输电线路巡检实时处理需求,例如参考文献[11]中的算法由于采用了三角网加密,且涉及多次点云遍历、大量点云数据迭代计算,使得电力线提取效率大大降低;参考文献[15]中的方法过程复杂、计算量大,对数据量或者区域大、点云密度高的情况,其效率和精度有待提高。
针对上述问题,简化电力线提取与重建流程,提出一种基于点云数据特征的电力线快速提取和重建方法,并解决电力线点云可能存在交跨线点云较难处理、绝缘子点云较难分割、现有算法模型研究不完整的问题。
-
提出从原始激光点云快速提取和重建电力线方法。电力线点云快速提取包括:首先,对原始点云进行粗分类,将原始点云中电力线点和部分噪点提取出来;然后,进行点云精分类,提取出精度较高电力线点云。电力线点云快速重建包括:首先进行电力线点云分割,将电力线点云分成单根,针对交跨线、绝缘子和x-O-y平面投影重合模型的点云特征进行数据分割;然后进行电力线重建,完成电力线矢量化。具体流程图如图 1所示。
-
对于现有方法多采用融合Hough变换、密度分析、机器学习分类等复杂算法进行电力线点云提取所导致的计算量大、耗时长问题,本文中通过研究电力线点云与输电通道其它非电力线点云之间的空间关系与区别特征,采用栅格划分结合高程阈值判定的简单高效方法对电力线点云进行快速的粗分类,并采用成熟高效的随机采样一致性算法(random sampling consistency algorithm, RANSAC)对电力线点云进行快速精化,最终实现电力线点云的快速提取。
-
电力线点云粗分类的目的是从原始输电线路点云中分割出电力线点云和少量其它类型点云噪点。输电线路原始点云主要包括电力线、地面、植被、杆塔,在高程方向上,电力线点云和地面、植被呈局部不连续分布状态[16-17]。针对输电线路点云这种分布特性,作者根据参考文献[16]中的部分思想,对原始点云创建3维体素栅格,采用设置合理高程阀值的方法快速分割出非电力线点云。3维体素栅格划分原理如图 2所示。
本文中将原始点云数据按照步长dx, dy沿输电线路走向x, y轴方向划分为n×m个3维体素栅格M(i, j)(i=1, 2, …, n; j=1, 2, …, m),如下式所示:
输电线路原始点云在高程方向分布情况主要有3种:地面、杆塔;地面、植被;地面、植被、电力线。从图中可以明显看出地面和植被点云呈连续分布状态,植被和电力线点云呈非连续分布状态。因此可以分割出地面点和植被点,保留电力线点云和杆塔点云。
(1) 创建3-D体素栅格。3-D体素栅格的尺寸会直接影响电力线点云提取准确率。3-D体素栅格过小,则每个栅格内点云数量过少,不能真实反映高程分布特征;相反会出现部分电力线点云被分为非电力线。经过大量输电线路原始点云实验验证,确定3-D体素栅格尺寸经验值为3m~5.5m效果最佳,本文中取4m。
(2) 确定3-D体素栅格内高程间隔尺寸。对于3-D体素栅格内按照高程分割,分割尺寸如果过大,可能会出现无法探测到非连续性特征,本文中采用3-D体素栅格的高程尺寸较小,如果高程方向上两个相邻3-D体素栅格内点云为空则合并这两个3-D体素栅格,新合并生成的3-D体素栅格的高程即为高程间隔,记为H。
(3) 计算高程阈值。设定一个高程间隔阈值H0,表示地面点和电力线的高程方向距离。对上一步H,进行高程阈值对比:如H < H0,把该网格内所有点判断为非电力线点云,如H>H0,记录该高程间隔的最小高程值Z0,对于3-D体素栅格中所有点Z值进行遍历,如果出现Z>Z0,即可判定该点为电力线点;否则判定为非电力线点。
栅格划分只需要遍历一次点云并仅进行坐标判断即可完成,高程阈值判定只需对栅格高程间隔与设定阈值进行比较分析即可完成,因此本文中点云粗分类算法的总体时间复杂度为O(n)。
-
原始点云数据在完成粗分类后,基本分割掉了地面点、植被点,得到了电力线、交跨线、部分杆塔点和部分噪声点云。电力线点云在x-O-y平面呈线性分布,杆塔点云在x-O-y平面呈明显的簇状分布,噪点在水平面呈散点分布。根据电力线、交跨线、杆塔和噪声点云分布特点,本文中采用随机采样一致性算法完成电力线、交跨线精提取,该算法根据包含异常数据的数据集计算出电力线、交跨线数学模型参量,得到有效电力线、交跨线数据的算法,具有较强稳定性。RANSAC算法原理[18-19]如图 3所示。
-
对于现有方法多利用悬链线方程、抛物线方程等对整条电力线中所有点云均参与重建拟合计算所导致的效率低问题,本文中采用分段、采样的思路,对电力线点云进行分段分割以及关键节点采样重建,以此避免对所有电力线点进行拟合计算,大大提高运算效率,实现电力线点云的快速重建,并对交跨线点云、绝缘子点云进行有效分割。
-
电力线点云精分类后,得到电力线、交跨线点云,两者在x-O-y平面投影均呈直线模型,本文中选用2维霍夫变换实现电力线、交跨线单根化,能有效解决电力线点云中断问题,提取电力线、交跨线,获取多个直线方程,根据直线方程统计电力线走向,将与电力线走向夹角较大的直线滤除,即可得到电力线点云,为防止出现交跨线、电力线夹角过小引起电力线漏检情况,针对电力线在输电通道长度较长,交跨线在输电通道长度较短这一特性,通过点云长度对比、点云数量阀值对比修正电力线分割结果。
此外,输电线路可能存在电力线x-O-y平面投影重合情况,针对这种电力线模型,单纯使用2-D霍夫变换,会出现电力线漏检[10]。因此,首先按照电力线走向对电力线点云按照一定步长进行分割,然后对分割后的电力线进行局部聚类[20],对聚类结果按照高程排序,最后对整档分割排序点云按照邻近点坐标近似相等原则进行合并,得到单根电力线。
在完成上述步骤后,电力线点云两端可能还包含部分绝缘子,而局部电力线点云可以近似看做3-D直线模型。因此,本文中在电力线两端采用3-D直线模型识别并提取高精度的电力线点云,剔除绝缘子点云。
-
为了解决常用重建方法中将所有电力线点云参与重建拟合计算,本文中采用提取局部加权质心的方式选取关键节点,以此实现对电力线点云的采样,并只对采样的关键节点进行拟合计算实现电力线重建,从而大大提高电力线重建效率,同时避免了噪声点对重建质量的影响。
设一条电力线点云在x-O-y面投影的重建直线为y=kx+b,遍历点云可获得电力线两个端点坐标,即(xl, yl)、(xr, yr)将电力线点云沿电力线走向划分为N段,则分割间距为:
局部质心计算公式为:
式中,i表示点编号;n代表点总数;m表示点权重,用该点到重建直线距离的倒数计算,即离重建直线距离越远,权值越小。
在完成单条电力线关键点提取后,进行电力线重建。本文中采用在x-O-z或y-O-z平面投影的多项式方程对局部电力线点云进行局部重建。根据最小二乘原理,重建过程可以转化为以下求S极小值问题。S表示投影坐标系内纵坐标实际值与计算值的误差平方和:
即:
式中, A, B和C分别表示多项式系数;xi, yi分别表示重建节点在投影2-D坐标系内的横纵坐标。∂S/∂A, ∂S/∂B和∂S/∂C是1阶偏导数。
1.1. 电力线点云快速提取
1.1.1. 点云粗分类
1.1.2. 电力线点云精化
1.2. 电力线点云快速重建
1.2.1. 电力线分割
1.2.2. 电力线重建
-
本文中选用Visual Studio 2013作为开发环境实现电力线分割算法。实验平台硬件配置:HP ZBook,CPU为Intel I7,内存32GB,装有Win10系统。采用南方电网A线路和B线路数据作为实验数据,两条线路基本情况如表 1所示。
data name voltage/
kVsegment number power lines number x-O-y plane projection number of point clouds A line 110 2 8 natch 1686608 B line 220 2 5 not natch 6586678 Table 1. Basic information table of transmission line
-
针对电力线x-O-y平面投影重合模型、绝缘子分割,采用南网A线数据测试,实验共耗时3.9s,对本文中提取的电力线点云数量进行统计,同时用CloudCompare手动精提取实际电力线点云,将两者进行对比,统计准确率,如表 2所示。图 4a为一级杆塔,图 4b为绝缘子分割前数据,可以明显看到导线末端的绝缘子,图 4c为绝缘子分割后电力线,可以清晰看到绝缘子基本剔除。
serial number of segment serial number of power line actual number of point cloud on the power line extraction number of point cloud accuracy rate/% 1 1-1 3805 3641 95.7 1 1-2 2605 2506 96.2 1 1-3 4819 4592 95.3 1 1-4 4258 4091 96.1 1 1-5 2776 2626 94.6 1 1-6 3289 3144 95.6 1 1-7 3334 3163 94.9 1 1-8 4343 4130 95.1 2 2-1 2946 2810 95.4 2 2-2 2951 2824 95.7 2 2-3 3206 3087 96.3 2 2-4 3842 3703 96.4 2 2-5 3549 3375 95.1 2 2-6 3241 3095 95.5 2 2-7 4267 4087 95.8 2 2-8 3276 3125 95.4 Table 2. Extraction results of power line of test data A
原始点云真彩色如图 5a所示,电力线重建效果如图 5b所示。
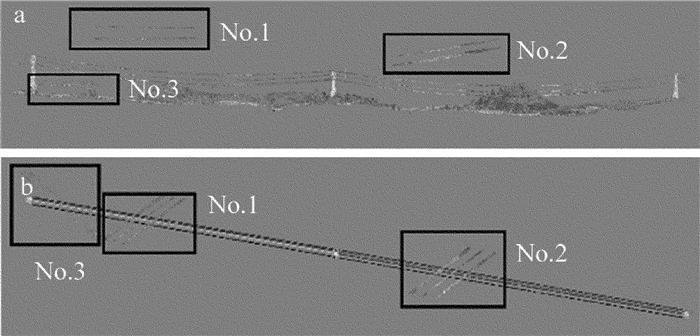
针对输电线路交跨,采用南网B线数据测试,如图 6所示有3处交跨,实验共耗时4.2s,对本文中提取的电力线点云数量进行统计,同时用CloudCompare手动精提取实际电力线点云,将两者进行对比,统计准确率,如表 3所示。
serial number of segment serial number of power line actual number of point cloud on the power line extraction number of point cloud accuracy rate/% 1 1-1 8933 8504 95.2 1 1-2 2724 2598 95.4 1 1-3 8905 8691 97.6 1 1-4 2496 2368 94.9 1 1-5 9511 9063 95.3 2 2-1 9041 8643 95.6 2 2-2 2876 2695 93.7 2 2-3 9746 9366 96.1 2 2-4 1892 1805 95.4 2 2-5 9678 9262 95.7 Table 3. Segmentation results of power line of test data B
原始点云真彩色如图 6a所示,电力线重建效果如图 6b所示。
通过对比电力线实际点云数据和算法提取数据,本文中的算法提取电力线时遗漏了少量电力线点,由于受到杆塔、绝缘子影响,提取的点云中还包含少量绝缘子点云。
-
将本文中的算法和已有方法一[11]和方法二[15]用相同实验数据作对比试验,并从电力线提取和电力线重建两大过程分别对比算法耗时。采用南方电网A线路和B线路作为实验数据,记录试验时间如表 4所示。
serial number of data method 1 method 2 method of this paper extraction time/s reconstruction time/s extraction time/s reconstruction time/s extraction time/s reconstruction time/s A line 6.6 3.8 4.1 3.8 1.3 1.0 B line 6.5 3.8 3.9 3.7 1.2 1.1 Table 4. Efficiency comparison
从表 4可以看出,对于南网A线、B线数据,方法一由于使用了融合Hough变换、主成分分析、密度分析等方法的复杂算法识别电力线点云,导致电力线提取时间较长,达到了6s以上,并选择了较为复杂的悬链线模型对所有点云进行拟合来重建电力线,使得电力线重建过程耗时也达到4s左右;方法二在电力线提取步骤由于采用了三角网加密算法,使得提取效率降低,但也略优于方法一,耗时4s左右,而在电力线重建步骤同样使用了悬链线模型对所有点云进行重建,重建效率与方法一一致;本文中方法基于电力线的空间特征,在保证电力线提取与重建准确度的前提下,采用了时间复杂度更低的简单高效算法进行电力线提取,耗时在1s左右,在电力线重建步骤,基于分段、采样的思路对关键节点进行多项式拟合重建,耗时也在1s左右,本文中方法总耗时在2.5s以下,效率优于方法一与方法二,实现了电力线的快速提取和重建。
2.1. 算法效果验证
2.2. 算法效率验证
-
提出了一种基于点云数据特征的电力线快速提取和重建方法,通过实验表明,本文中的方法不仅在精度上可以满足架空输电线路安全距离分析应用,而且在效率上可以满足输电线路机载激光巡线的实时处理需求,此外,对电力线空间排列方式、交跨线干扰、绝缘子干扰等因素不敏感,算法鲁棒性较高。经大量断裂电力线点云数据测试,算法综合准确率达到95.3%,总体耗时达2.5s以下,工程适用性较强。

 Map
Map










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: