HTML
-
激光二极管(laser diode, LD)抽运的调Q固体激光器具有转换效率高、光束质量好、重复频率高、峰值功率大和结构紧凑等优点,在激光雷达、激光精密加工、光通信、激光测距及生物医疗等诸多领域均有着十分重要的应用[1-3]。目前基于声光调Q激光器获得较窄激光输出脉宽的主要方法有[4-8]:提高抽运速率,调节抽运光与谐振腔内振荡光的匹配系数,缩短腔长,减小Q开关启闭速度等,其中的前两个方法是为了增大反转粒子数密度,提高谐振腔内的增益系数,而减小Q开关启闭速度则需要考虑调Q过程中所引入的两类阈值[9]。第1类阈值是在声光Q开关拥有高声光衍射效率时的阈值,此时谐振腔处于高损耗的状态;第2类阈值是声光Q开关在打开状态时激光不发生衍射时的阈值,此时激光器输出脉冲。第一阈值须保证在Q开关打开之前,谐振腔内的振荡光不起振,如果衍射效率不足,即射频(radio frequency, RF)功率较小时,腔内总损耗将会小于腔内总增益,就会出现漏光现象,此时的Q开关将不能完全关断振荡光振荡。第2类阈值会影响脉冲的大小、形态、脉冲的建立时间。在第2类阈值处,即在打开Q开关时,腔内损耗不能立即稳定在最低值,在超声波消失过程中,损耗就会一直处于变动之中,因为激光脉冲时间较短,当脉冲完全输出后,损耗却不一定会降到最低值,这将会影响出射激光脉冲的时间特性。本文中重点研究了高重频(100kHz)纳秒脉冲Nd: YVO4激光器的输出特性随RF信号功率的变化规律,实验得出了既保证门信号开启后激光脉冲序列具有一定的“上升”速度、又不会导致漏光过于严重的最佳射频信号的功率范围。所得到的研究结论对构建用于激光加工的快速开启式调Q脉冲固体激光器具有较为重要的参考价值。
-
声光调Q技术的基础理论是电声转换和声光效应。调Q过程通过调节激光谐振腔内的衍射效率来界定腔内损耗和反转粒子数分布,从而调节激光脉冲的脉宽与峰值功率等激光输出特性[10-13]。一般说来,RF信号的功率如果发生改变,则声光晶体所接收的超声波功率会发生变化,其相应的衍射效率也会随之发生改变。Q开关的关断,其阈值由衍射效率决定,衍射效率越高,损耗越大,相应的阈值也越大。Q开关打开时,激光的振荡阈值迅速减小,最后逐渐稳定到最小值[14],其稳定时间受开关前后阈值大小的影响。下面对该过程进行具体的分析。
-
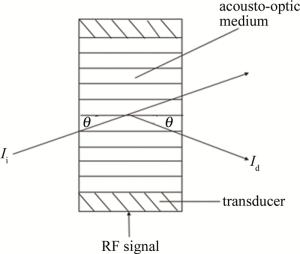
声光介质的衍射原理如图 1所示。图中, Ii为入射光强,Id为衍射光强,θ为入射角。在声光Q开关(acousto-optic Q-switch, AOQ)的介质中,射频功率产生高频振荡信号,并通过换能器转换为声波信号,使声光介质折射率发生变化,形成了等效的相位光栅。光束这时通过介质时,就会产生布喇格衍射,其衍射效率为[15]:
式中,P为超声功率,M为声光品质因素,L/h为换能器长宽比,λ为抽运光波长。超声功率较高时,Q值较高,损耗也较大,当光腔内的总损耗大于增益时,腔内的光振荡停止,反转粒子数逐渐积累,腔内总损耗因子为[16]:
式中,δ0为腔内固有损耗,-ln(R1R2)为耦合损耗,其中的R1, R2为两反射镜的反射率,-2ln(1-η)为Q开关的衍射损耗,η是衍射效率。激光的振荡阈值可表示为[17]:
式中,σ为受激发射截面,L0为增益介质长度。如果衍射损耗小于腔内增益,即初始粒子数反转的数目ni>Nt,则在谐振腔内就会有振荡的激光产生,同时也会发生漏光现象[18]。
-
Nd: YVO4激光具有四能级系统,其谐振腔内光子密度与粒子数反转密度的速率方程为[19]:
式中,R(x, y, z)为抽运速率密度,ΔN(x, y, z)为反转粒子数密度,S(x, y, z)为腔内光子数密度,S=∫∫∫S(x, y, z)dV为腔内总光子数,t是时间,${\frac{c}{n}}$为晶体中的光速,n是折射率,V为晶体体积,τc为光子寿命,τf为增益介质的荧光寿命, σ为受激辐射截面。
当系统稳定运行时,$\frac{{{\rm{d}}\Delta N(x, y, z)}}{{{\rm{d}}t}} = 0$,$\frac{{{\rm{d}}S}}{{{\rm{d}}t}} = 0$。其输出功率为[20]:
式中,T为输出耦合镜的透射率,l为谐振腔长度,hν0为振荡光子的能量。由于Q开关打开时存在衍射效率的延迟过程,腔内损耗不能够马上稳定在最低值,这就使得第二阈值不够稳定,因为激光脉冲的时间较短,在腔内损耗还没有达到最低时,脉冲可能就已经完成。衍射损耗越高,损耗降到最低的时间也就越长,所以在Q开关打开之后,由于损耗较大,激光输出功率比较低,之后逐渐升高并趋于稳定,即Q开关打开后激光开启会出现延时。
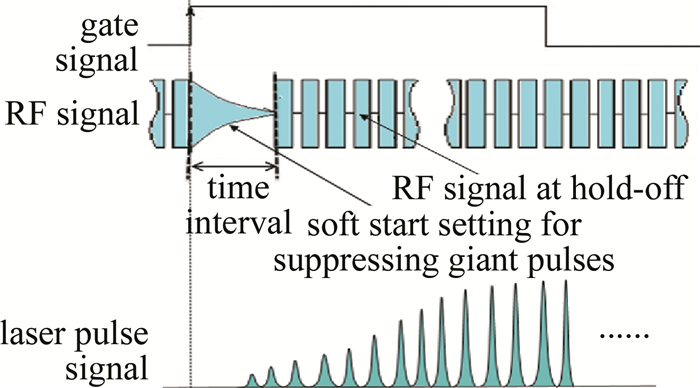
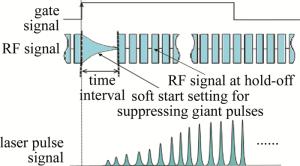
门信号、射频信号以及激光输出的脉冲序列信号之间的相互关系如图 2所示。由于对实用型连续抽运声光调Q激光器来说都需要抑制首个巨脉冲, 一般主要都是通过选择适当的呈右向类三角变化的RF信号时间间隔(见图 2)来进行抑制。时间间隔越短,抑制效果就越不佳。本实验中此时间间隔选定为15ms。另外,漏光大小与此时间间隔没有直接关系。作者将在后续的文章中报道,在门信号开启后这个时间间隔与Nd: YVO4激光不同的偏振态之间的复杂物理关系。
1.1. 衍射效率与漏光的关系
1.2. 空间速率方程
-
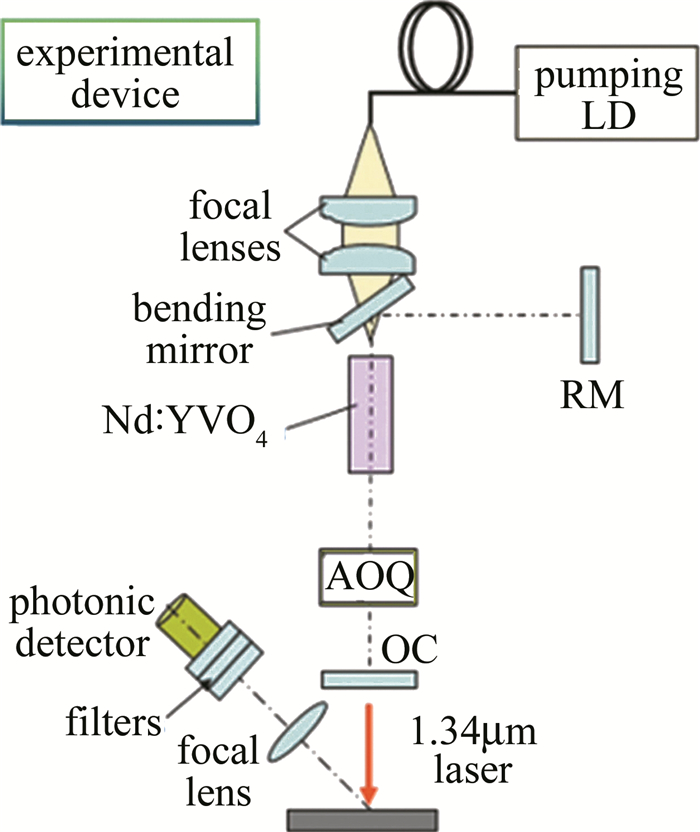
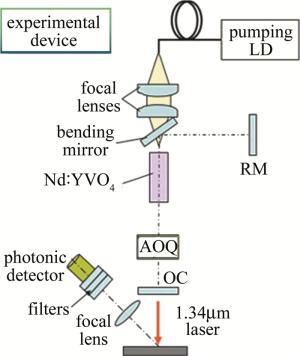
实验装置如图 3所示。采用LD端面抽运的声光调Q激光器,激光增益介质为Nd: YVO4晶体,由平面输出耦合镜(output coupler, OC)、全反射镜(rear mirror, RM)和倾斜平面镜组成的L型谐振腔,腔长为130mm,脉冲激光的1.34μm输出信号是经过焦距为120mm的凸透镜聚焦后,经由数枚衰减片减弱后由光电探测器(photonic detector, PD)接收。
-
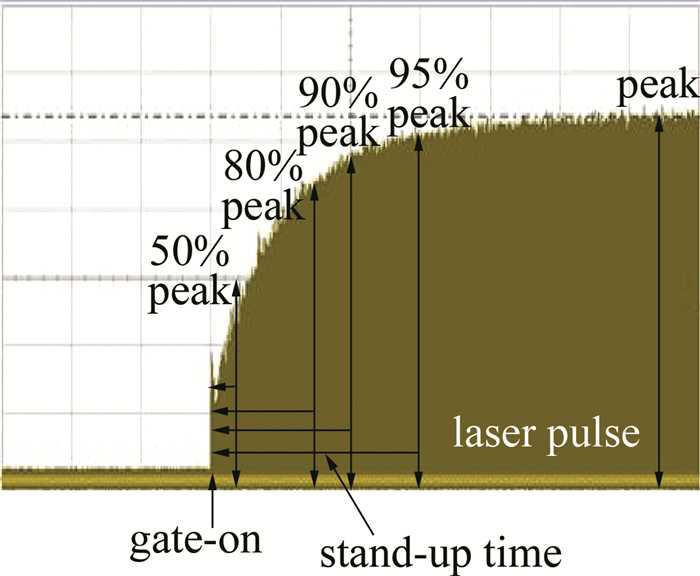
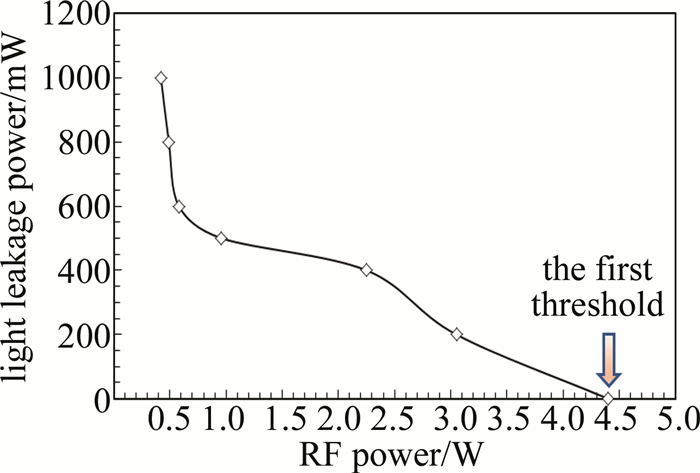
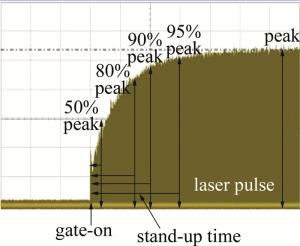
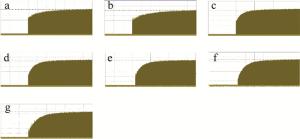
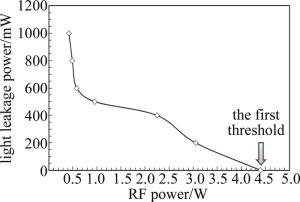
门信号是激光加工过程中控制激光脉冲串输出的外部电气命令信号,任何固体激光由于热效应的相对滞后,不可能对电气门信号达到“即答即应”的响应速度。而对于1.34μm的Nd: YVO4激光而言,更由于其存在着严重的激发态吸收(excited state absorption, ESA),激光晶体的热效应远比一般的Nd: YAG激光要严重得多。这就使得在门信号开启后的一段时间内,输出的激光脉冲序列会呈现逐步增强的趋势。尽可能缩短这个上升时间是激光加工过程中的一个重要的工程性要求。门信号开启后序列激光脉冲串不同的上升时间的定义如图 4所示。分别测试了高重复频率(100kHz)下声光Q开关在不同的射频功率(PRF分别为0.42W, 0.49W, 0.58W, 0.96W, 2.25W, 3.05W, 4.40W)条件下所分别对应的漏光功率与门信号开启时的序列激光脉冲的上升波形(见图 5),相应的最终结果被归纳到表 1中。对表中数据进行拟合,可得到门信号关闭时的漏光功率随RF功率的变化曲线(见图 6),从图 5和图 6可以看出,Q开关处于关闭状态时的漏光功率随RF功率的增大而减小,在RF功率较小时,漏光功率的变化较快,而在RF功率达到4.4W时,漏光完全消失,这就是所谓的第一阈值。这是由于在抽运速率一定时,反转粒子数受限于腔内总损耗,在RF功率较低时,衍射损耗较小,腔内总增益大于总损耗,存在着较为严重的漏光现象;而当RF功率提高到一定程度时,漏光自然也就消失了。
PRF/W leakage
power/mWrise time/ms 50% peak 80% peak 90% peak 95% peak 0.42 1000 0 15 32 55 0.49 800 0 20 48 72 0.58 600 0.8 23 62 110 0.96 500 8 35 70 115 2.25 400 10 42 80 120 3.05 200 15 52 88 132 4.40 0 20 65 100 150 Table 1. The leakage power and the rise time of the output pulse under different RF power
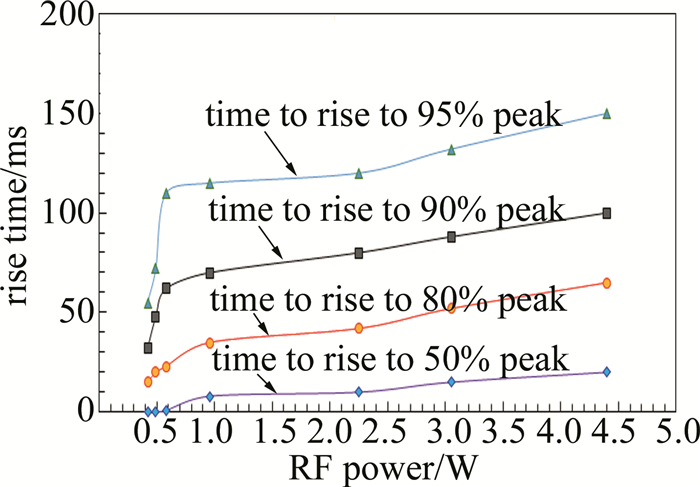
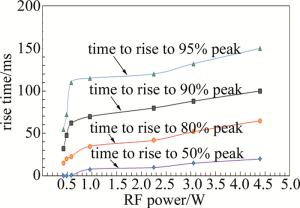
通过拟合还可得到门信号开启后激光序列脉冲的上升时间随RF功率变化曲线(见图 7)。从图中可以看出,在RF功率小于0.5W时,脉冲很快就能达到峰值输出的50%;随着RF功率的增大,激光序列脉冲的上升时间逐渐增大,在RF功率达到0.58W之前,激光序列的脉冲上升时间变化很快,而在之后则变化较慢。这可以解释为:在RF功率较低时,腔内损耗较低,由于漏光原因,腔内反转粒子数密度也较小,而在Q开关彻底打开后,腔内损耗能够较快达到平衡,脉冲上升时间也就随之变短。
在构建用于激光加工的快速开启式调Q脉冲固体激光器时,需要同时顾及门信号“开启”后激光脉冲序列的上升速度和较低的漏光功率,选择较为合适的射频信号功率范围就具有较为重要的工程实用价值。单就本文中的实验系统来说,RF信号功率位于2W~3W之间时,漏光功率在500mW以下,门信号开启后激光脉冲的上升时间大约只是第一阈值时的60%~70%左右,应该满足大部分快速门信号开启的快速激光加工要求。
2.1. 实验装置
2.2. 实验结果与分析
-
首先理论分析了固体激光器的声光调Q过程,推演了在Q开关hold-off状态时衍射效率与激光系统漏光的关系。然后,通过实验测量了LD抽运1.34μm Nd: YVO4声光调Q激光器的漏光特性和输出激光脉冲序列的上升时间随RF功率的变化,并对该结果作了系统分析。分析结果表明,RF功率的提高不仅能减小漏光功率,也同时会增大激光输出脉冲序列的上升时间,所以,在构建用于激光加工的热效应比较严重的调Q脉冲激光器时,并非一定要完全消除漏光,而是应该根据实际情况选择合适的RF功率来同时获得较高的激光的开启速度。

 Map
Map




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: