HTML
-
液位是很重要的测量参量,在生活中的很多方面都需要进行液位的测量。如对飞机、汽车、轮船的油位测量,可以大大实现油量的节省,对节约能源起到了重大帮助[1]。常见的液位测量方法有机械浮子式液位传感、电容式液位传感[2]、液压式液位传感、超声波式液位传感[3]、磁致伸缩式液位传感等[4]。传统的电子、机械类液位测量仪,存在着各自不同的问题,例如易受到外界环境的干扰造成损坏,导致成本提高等一系列问题,因此不适用于一些恶劣环境[5]。
常见的光纤式液位测量方法有功率泄露式、模式干涉型[6]、液面反射型等[7]。普遍使用的方法是模式干涉型,即在外界因素干扰的情况下会改变不同纵向传播系数的高阶模式折射率,使得传输光的透射谱波长发生变化,通过传输光透射谱的波长漂移与外界液位的关系来解算出外界液位信息[8]。在光纤液位测量的发展历史中[9],经过科研人员的不断努力,光纤液位测量发展迅猛,现已有各式各样的光纤液位传感器。例如阿威罗大学的一种基于多模干涉和光纤光栅的液位测量传感器[10]; WANG等人的快轴方向纤芯错位熔接的液位测量传感器[11]; 武汉理工大学的高双折射环境的光纤液位传感器[12]; 重庆理工大学的无芯光纤强度调制型液位传感器[13]; 西安石油大学的在线型光纤迈克尔逊干涉仪[14]; 北京交通大学的高折射率液位传感器[15]; 吉林大学的全光纤干涉式水位传感系统[16]。
本文中所设计的是一种基于空芯光纤多模干涉效应的液位传感器,该传感器所使用的结构为单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤。主要通过探究外界液位变化所引起的光源在空芯光纤中多模干涉所产生的干涉谱的变化的关系,然后通过干涉谱的变化来确定液位的变化。
-
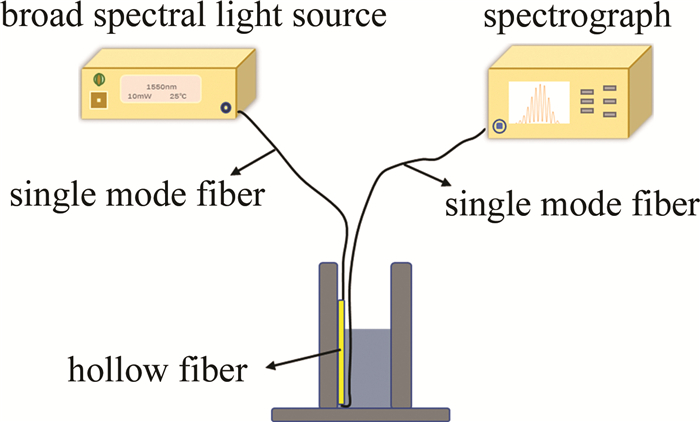
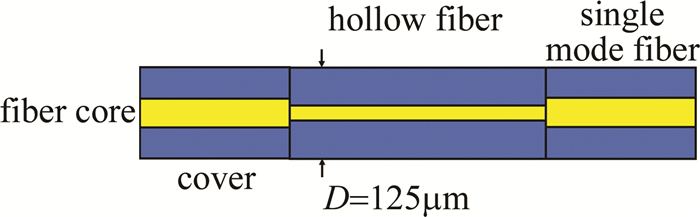
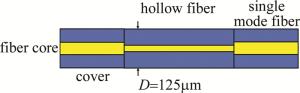
该光纤液位传感器由两端两根单模光纤和中间一根空芯光纤熔接而成,其结构如图 1所示。
图 1中两端的单模光纤所使用的是美国康宁公司的单模光纤,型号为G652D,纤芯为9μm,该单模光纤除去涂覆层后的外径为125μm。传感器结构中间部分的空芯光纤使用的是Polymicro Technologies公司的TSP005150纯石英空芯光纤,内径为5μm,除去涂覆层后外径D=125μm,它是一种典型的模式干涉型传感器,当光源发出的光从单模光纤传输到空芯光纤时, 会因为单模光纤与空芯光纤的纤芯直径不同发生模式失配效应, 在空芯光纤中激发一系列的高阶模式,不同的高阶模式相互之间发生模式干涉。
制造传感器时, 首先剥去两端的两根单模光纤的端部部分涂覆层,然后使用光纤切割刀切割端面,使得端面切割平整。对空芯光纤的涂覆层使用火焰快速烧过,去除涂覆层后, 使用切割刀将空芯光纤端面切割平整,然后通过光纤熔接机将两根单模光纤切割过的端面分别熔接在空芯光纤的两端。将一根单模光纤未切割过的一端连接在宽光谱光源上,另一根单模光纤未切割过的一端接在光谱仪上边。通过光谱移动和液位的线性关系来解算出液位的变化。
-
宽光谱光源发出的光在单模光纤与空芯光纤的连接处会因为单模光纤与空芯光纤的纤芯直径不同而发生模式失配效应,从而产生不同高阶模式的传输光,这些高阶模式依据各自不同纵向传播常数在传感器中段的空芯光纤中继续传播,并且这些不同纵向传播常数的高阶模式在空芯光纤中会发生模间干涉。根据多模干涉理论可知,透射谱中的自映像峰值波长可以表达为[17]:
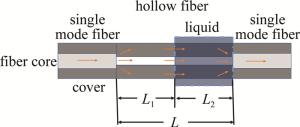
式中, n为空芯光纤的有效折射率,P为自映像系数,DHF为空芯光纤有效模场直径,L为空芯光纤长度。由表达式可知, 自映像峰值波长λ0与空芯光纤的长度L、有效折射率n、有效模场直径DHF有关。当空芯光纤长度L不变,外界环境温度、折射率等发生变化时,均会改变空芯光纤的有效折射率n,从而造成自映像峰值波长发生变化[18]。所以当空芯光纤的部分被浸没在液体中时,峰值波长由露在空气中的部分和浸没在液体中的部分决定[19],其结构如图 2所示。
表达式为:
式中,n1为空芯光纤暴露在空气中的有效折射率,DHF, 1为空芯光纤暴露在空气中的有效模场直径,L1为空芯光纤暴露在空气中的长度,n2为空芯光纤浸没在液体中的有效折射率,DHF, 2为空芯光纤浸没在液体中的有效模场直径,L2为空芯光纤浸没在液体中的长度。式中L=L1+L2, 所以表达式可以简化为:
当液体介质均匀,折射率保持稳定时,即空芯光纤浸没在液体中的有效折射率n2与空芯光纤浸没在液体中的有效模场直径DHF, 2保持不变,干涉谱的自映像峰值波长λ0与空芯光纤浸没在液体中的长度L2成正比关系。
-
为了研究单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤结构的传感器干涉谱随着液位变化的移动,设计了如图 3所示的实验。整个系统由宽光谱光源、单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤的传感器结构、光谱仪组成。实验中所用的宽光谱光源为超辐射发光二极管(super luminescent diode,SLD),该宽光谱光源的输出波长范围为1440nm~1660nm, 带宽为90nm。由宽光谱光源SLD在600mA电流的驱动下发出的中心波长为1568nm光进入单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤的传感器结构,然后通过光谱仪来记录出干涉谱的位移。在单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤的传感器结构中,空芯光纤的长度为55mm,即该传感器的可测量范围为0mm~55mm。实验中使用的待测液体为n=1.33的蒸馏水和n=1.35、质量分数为0.10的NaCl溶液。所使用的光谱仪为日本Antitsu公司的MS9740A型号。
在实验开始后向容器中加入蒸馏水, 使得蒸馏水浸没传感器结构的空芯光纤部分,此过程中每5mm向容器中加一次蒸馏水测量,一共测得12组数据点位,图 4是在被测液体选取为蒸馏水时, 蒸馏水的液面高度每上升5mm用光谱仪记录一次干涉光谱曲线。图 4中记录的是液面高度从0mm增加到55mm时,每5mm记录一次的干涉光谱曲线总图及其局部放大图。从图 4可知, 除了自映像峰外还有多个谐振峰,随着液位高度的升高整个干涉光谱曲线向波长增大的方向移动,并且峰值以及形状变化微小,这表明: 在液位上升过程中,单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤传感器结构的干涉谱发生了波长漂移,透射功率变化几乎忽略不计。
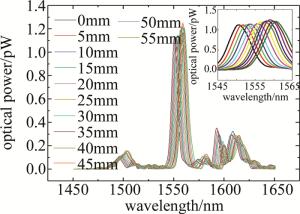
Figure 4. Spectrogram of spectrometer measurement spectrum with distilled water level variation spectrum
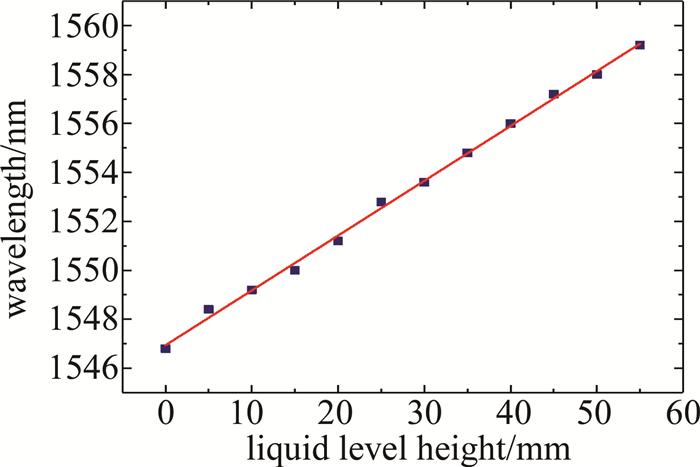
在图 4的多个干涉谱中以自映像峰值波长作为研究对象, 选取液位在0mm~55mm中液位每增加5mm时对应液位下的自映像峰值波长,绘制其自映像峰值波长随液位变化的关系, 如图 5所示。由图 5可知,自映像峰值波长随液位的增加匀速向长波长方向漂移,液位每上升5mm自映像峰值波长向波长增大方向漂移1nm左右,在液位上升过程中共向长波长方向漂移10nm左右,其线性度R2=0.9957,蒸馏水液位测量灵敏度为0.180nm/mm。
选取测量液体为质量分数为0.10的NaCl溶液,依照上述测量方法对单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤的传感器结构从0mm~55mm的高度逐渐加入质量分数为0.10的NaCl溶液, 然后通过光谱仪每5mm记录一次干涉光谱曲线图和数据, 共计12组。图 6所示为光谱仪在液面高度从0mm~55mm每5mm记录一次对应的质量分数为0.10的NaCl溶液液位下的干涉光谱曲线图样以及其局部放大图。图中,横坐标为波长,纵坐标为光功率。
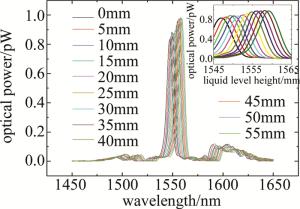
Figure 6. Spectrogram of the measured spectrum of the spectrometer with the change of the level of NaCl solution with mass fraction of 0.10
在图 6的多个干涉谱中以自映像峰值波长作为研究对象, 选取液位在0mm~55mm中液位每增加5mm时对应液位下干涉谱的自映像峰值波长,绘制其自映像峰值波长随液位变化的关系如图 7所示。由图 7可知, 自映像峰值波长在液位上升过程中共向长波长方向漂移12.4nm,其线性度R2=0.998,质量分数为0.10的NaCl溶液液位测量灵敏度为0.224nm/mm。
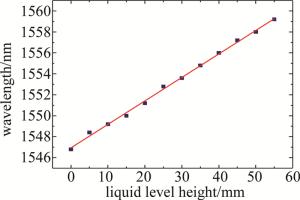
Figure 7. Peak wavelength of the self-image varies with the level of NaCl solution with mass fraction of 0.10
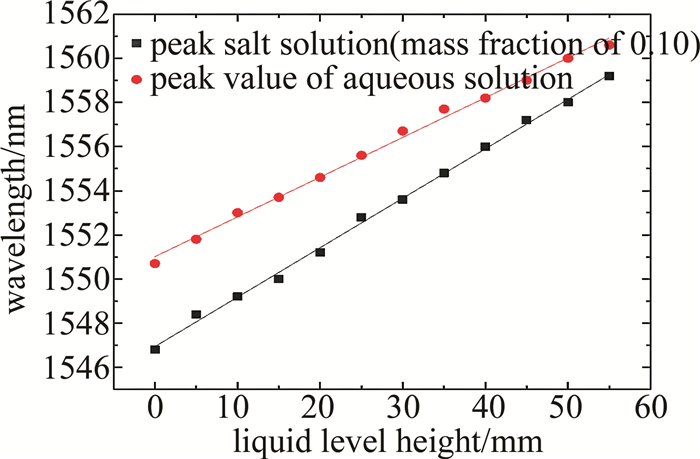
由(3)式可知,单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤结构的液位传感器的灵敏度与空芯光纤的长度以及液体的折射率有关,当空芯光纤长度固定时,浸没不同折射率的液体,可以得到不同的液位灵敏度,通过观察蒸馏水和质量分数为0.10的NaCl溶液中透射光谱波长漂移和液位变化关系来判断液体折射率对单模光纤-空芯光纤-单模光纤结构的液位传感器灵敏度的影响。根据蒸馏水和质量分数为0.10的NaCl溶液所测的透射光谱波长漂移和液位变化关系, 如图 8所示。由图 8可知, 浸没不同折射率的液体时,均有较好的线性度。当液体的折射率增大时,空芯光纤在液体中的有效折射率n2增大,且与空芯光纤在空气中的有效折射率n1之差越大,液位测量灵敏度就越高[20]。所以当空芯光纤长度一定时,可以根据浸没不同液体时透射光谱波长漂移与液位高度关系的灵敏度曲线来判断液体折射率的大小, 即灵敏度越高,液体折射率越大; 灵敏度越低,液体折射率越小。
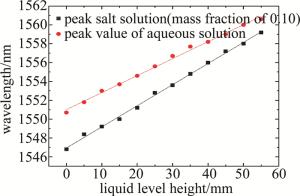
Figure 8. Relationship curve between the wavelength shift of distilled water and NaCl solution with mass fraction of 0.10 and the liquid level
该传感器在做实验时使用的测量液体为蒸馏水和自己配置的NaCl溶液,配置NaCl溶液时难免导致液体介质不均匀,使得测量结果产生偏差。在实验增加液体过程中杯子刻度最小单位为mm,而增加液体时是人眼观察液面上升情况,会产生不可避免的毫米内的液位高度差,使得测量结果产生误差,而且在增加液体时,会发生水面迸溅现象,使得液滴迸溅在未被水面浸没的部分,产生测量误差。数据计算过程中在微小的波长段里会有峰值相同的峰,所以, 在数据选用过程中, 采取计算均值的方法减小误差。
-
提出了一种液位传感系统, 主要是基于空芯光纤中多模干涉效应的液位传感系统,并做了相应的理论和实验研究。首先介绍了光纤液位传感器的应用、分类以及目前的繁多研究现状。其次介绍了该光纤液位传感器的主要结构以及该光纤液位传感器的制作过程。然后讲解了该液位传感器测量液位的原理。最后搭建了基于空芯光纤中多模干涉效应的液位传感实验,实验研究了该液位传感器的干涉谱与液位变化的关系以及不同折射率液体对测量结果的影响,并且分析了实验误差。实验结果表明,该光纤液位传感器的液位测量范围为0mm~55mm,液体折射率为1.33和1.35时,液位测量灵敏度分别为0.180nm/mm和0.224nm/mm。该传感器具有良好的液位测量功能,且结构简单、易搭建,可以应用在一些测量微小液位变化的情况中。

 Map
Map





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: