HTML
-
自20世纪90年代以来,啁啾脉冲放大技术的出现给激光技术领域带来了巨大进步。在激光与物质相互作用领域,超短激光脉冲因其具有产生阿秒级X射线甚至γ射线脉冲的潜力而成为研究的焦点[1-3]。这种超短脉冲使得在飞秒到阿秒级别内研究亚周期动力学成为可能。在强激光场的环境下,电子的运动过程具有相对性特征,这使得非线性辐射过程中,入射激光脉冲的各种参数,如偏振态、束腰、脉冲宽度、初始相位以及不同的电子初始状态(初始速度、初始位置等)将导致电子轨迹和辐射特性产生明显的差异。
在非线性汤姆逊散射中,科学家和专家针对不同的参数进行了各种研究[4-7]。例如,在激光强度方面,WANG等人[5-8]研究了激光的运动和空间辐射特性,发现随着激光强度的降低,最大辐射方位角及其发散度随着速度的不同而增加。对于不同的偏振激光,YU等人[9]研究了线偏振激光脉冲,CHEN等人[10]研究了圆偏振激光,他们从研究中得出了不同的结论。此外,BOCA等人[11-13]研究了极强激光脉冲对超相对论电子的散射,并针对短激光脉冲讨论了载流子包络相位效应,最终提出了两个尺度定律以预测广泛的参数的角分布行为。现有文献中对大多数相关参数进行了各种研究,然而对于圆偏振激光作用下的初始位置的研究还存在空白,故作者对不同初始位置的圆偏振紧聚焦激光脉冲与静止电子之间的作用机理进行了深入的研究。
本文中研究了电子初始位置对圆偏振激光脉冲中高能电子运动的空间轨迹及其空间角辐射特性的影响。通过将2维(θ, ϕ)和3维xyz分析相结合的方法进行数值模拟。结果表明,电子在圆偏振激光作用下的空间轨迹呈螺旋状,分为前部紧密螺旋状和后部稀疏圆两部分;电子运动的空间角辐射呈分离螺旋状,且随着初始位置的右移逐渐发散分离。
-
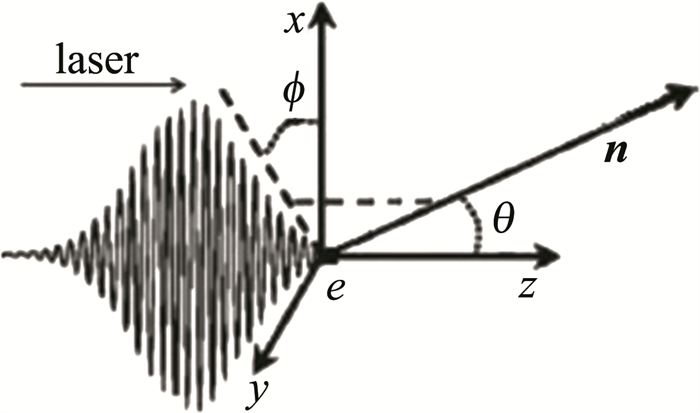
在非线性汤姆逊散射模型中,对于圆偏振激光考虑了由高斯型包络建模[14-15]。紧聚焦激光与电子相互作用的几何示意图如图 1所示。为了便于分析描述,作者做出如下假设:+z轴延伸方向是图中圆偏振激光脉冲的传播方向,一个电子位于坐标原点上,并且在作用前保持静止状态,当激光脉冲到达坐标原点,与该电子相遇时,受到了激光电场的作用,电子不仅在横向做高频振荡,也会在激光脉冲的有质动力推动下向前运动[16-17]。在电子和激光脉冲二者相互作用时,各个方向都有由电子发出的谐波辐射[18],如果用n来表示电子的辐射方向,那么它的表达式为n =sinθ· cosϕ· x +sinθ sinϕ· y +cosθ· z (极角θ和方位角ϕ如图 1所示)。
由相关理论知识[7]公式推导所得结论,在3维坐标系中,紧聚焦圆偏振激光脉冲电场的矢势可以表示为:
式中,a0是已经归一化的激光强度振幅, 表达式为a0=eA0/(mc2)=0.85×10-9$\sqrt {I{\lambda _0}^2} $,m, e分别为电子静止时的质量和电量,A0为激光场矢势的振幅,c为光速,I为激光强度峰值,波长λ0=1 μm;L和w分别是圆偏振激光的脉宽和束腰半径, w0是脉冲的最小束腰半径;η=z-t,ρ2=x2+y2是传播方向的垂直距离。
为了便于分析,矢势的正交分量的大小可以表示为:
圆偏振紧聚焦激光脉冲的相位φ在3维坐标系下可以表示为:
式中,C0是啁啾系数(本文中C0=0,不考虑啁啾), φ0是激光脉冲的初始相位,φG是受波阵面曲率影响的Guoy相位,φR是与曲率半径相关的相位,它可以通过以下公式表示:
式中,R(z)是脉冲激光波前的曲率半径,可以表示为:
根据电子的能量方程和拉格朗日方程[7-10],可以将电子在电磁场中的运动表示为:
式中, v为利用光速c进行归一处理的电子速度,a为被mc2/e所归一化的矢势,p =γv为利用mc进行归一化的电子动量,相对论因子γ=(1- v2)-1/2,也就是由mc2进行归一处理的电子能量。而(7)式中的哈密顿算子▽a只作用在a上。
根据(2)式,微分方程(6)式、(7)式可分解得到如下4个微分方程:
式中,vx,vy和vz分别表示电子在3个坐标轴方向上的速度分量的大小;ax、ay和az分别表示电子在3个坐标轴方向上的加速度分量的大小。利用MATLAB程序求解上述的4个微分方程,可分别求出电子在激光场中的坐标、速度、加速度和能量随时间变化的改变量。
-
由电动力学知识,结合参考文献[19]和参考文献[20]中所得相关结论以及第1.1节中所作出的讨论可知,以相对论速度作加速运动的电子会放出电磁辐射,单位立体角内的辐射功率可以表示成:
式中,n为辐射方向的单位向量,P(t)为辐射功率,Ω为立体角,t′是圆偏振激光脉冲与电子相互作用的时间,t是观察点所处的时间,即t=t′+R。R=R0- n · r,R0为观察点距离电子与圆偏振激光脉冲相互作用点的距离,r是电子位置矢量。
因此,单位立体角的总辐射能量可以由所有有效辐射的积分表示,即:
式中,W为总辐射能量。
1.1. 圆偏振紧聚焦激光脉冲矢量势
1.2. 角辐射
-
与理论分析中提到的部分一致,圆偏振紧聚焦激光由高斯型包络建模。运用4阶Adams和Runge-Kutta的计算方法,可以得出电子从被激光脉冲前沿超越的点到离开后沿的轨迹。选取沿+z轴传播的激光脉冲进行计算模拟,其中波长λ0=1 μm,最小束腰半径w0=3λ0,脉冲宽度L=3λ0(10 fs),激光强度振幅a0=5,激光偏振参数δ=1。
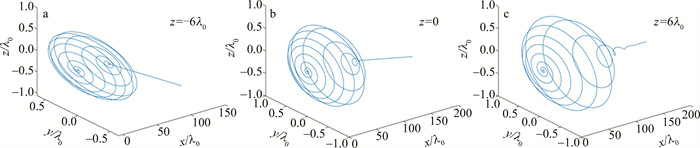
分别用k-1和ω0-1来对电子空间和时间坐标进行归一处理,其中k表示波数,ω0表示激光频率。初始相互作用时,参考系原点处的静止电子距离激光脉冲中心距离为5L。在线偏振紧聚焦激光与电子相互作用时,电子的运动被限制在平面内。然而,在圆偏振激光的情况下,电子的轨迹不再局限于平面,而是延伸到3-D坐标,涡旋角动量驱动电子作螺旋运动。
图 2和图 3表明,电子的运动轨迹和空间角辐射对电子初始位置变化的高度敏感。首先,图 2展示了电子初始位置分别在-z轴方向6个波长处、z=0处以及+z轴方向6个波长处时,电子在全空间中的运动轨迹。根据(8)式~(10)式,可以得出电子在涡旋横向力的作用下在全空间运动的前部轨迹呈紧密分离螺旋状,而后部轨迹由空间间隔遥远的稀疏圆组成。但是这种轨迹围绕+z轴的对称性随着电子初始位置的右移逐渐消失,这是由于紧聚焦激光内部的长时间相互作用引起的电子轨迹的偏移。因为紧聚焦强激光内部的长时间相互作用,沿+z轴的有质动力加速度激发了电子,使之具有超快速度vz,引起了电子运动轨迹后部的不规则加速过程。由于+z轴的巨大规模,放大了横向减速过程并缩小了导致不规则运动的加速过程。同时,随着初位置的左移,不规则加速轨迹逐渐近似直线运动。作者还发现,这一直线运动的方向随着初位置的左移也发生了逆时针的偏转。

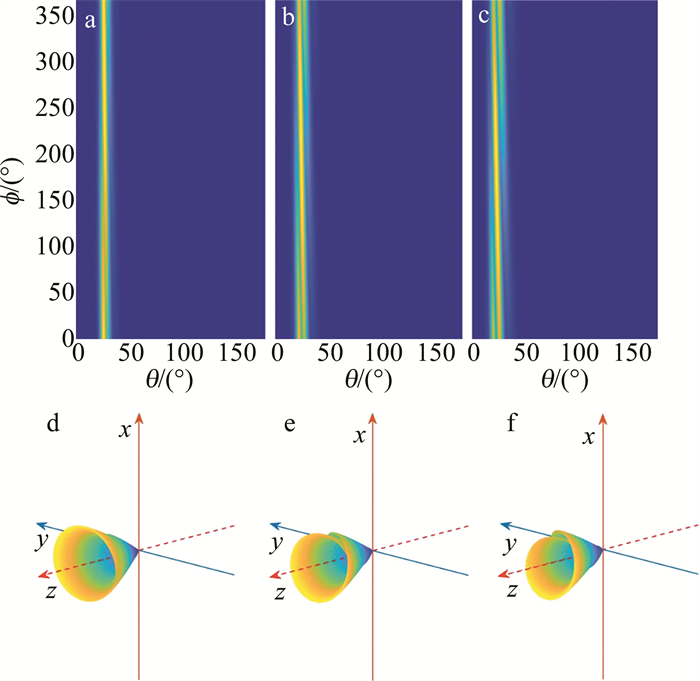
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of spatial angular radiation analysis of electrons at different initial positions
其次,图 3展示了在不同初始位置下电子的空间角辐射分布。从图 3a~图 3c可以明显看出,辐射中心在一个方位角范围内,辐射方位角和方位角的旋转发散随着初始位置沿+z轴方向移动,同时也可以观察出,辐射在(θ, ϕ)平面是斜绘的孤立条纹,且随着初始位置的右移,孤立条纹现象越清晰,即电子的辐射峰值功率双峰现象逐渐明显。这是由于电子初始位置的右移,电子辐射脉冲的个数相应增加,进而使得其辐射功率增加。从另一个角度来观察,角辐射也是一个3维xyz图,从图 3d~图 3f中可以发现,其3维形状是从边缘延伸的分离螺旋最终缩回内部,电子空间角辐射情况整体看起来更像是一个花瓣,边缘有小起伏,且随着初始位置的变化发生了明显的改变,这种现象与(θ, ϕ)平面上发生的变化有着密切关联。这是因为在强激光中,电子获得了超相对论性的能量,很大程度上减少了空间能量的耦合,即在速度扫过的方位角范围内,在(θ, ϕ)平面存在具有一定θ值的ϕ角度间隙。由于强激光中电子运动距离z轴很远,使得图 3a~图 3c中光带倾斜。
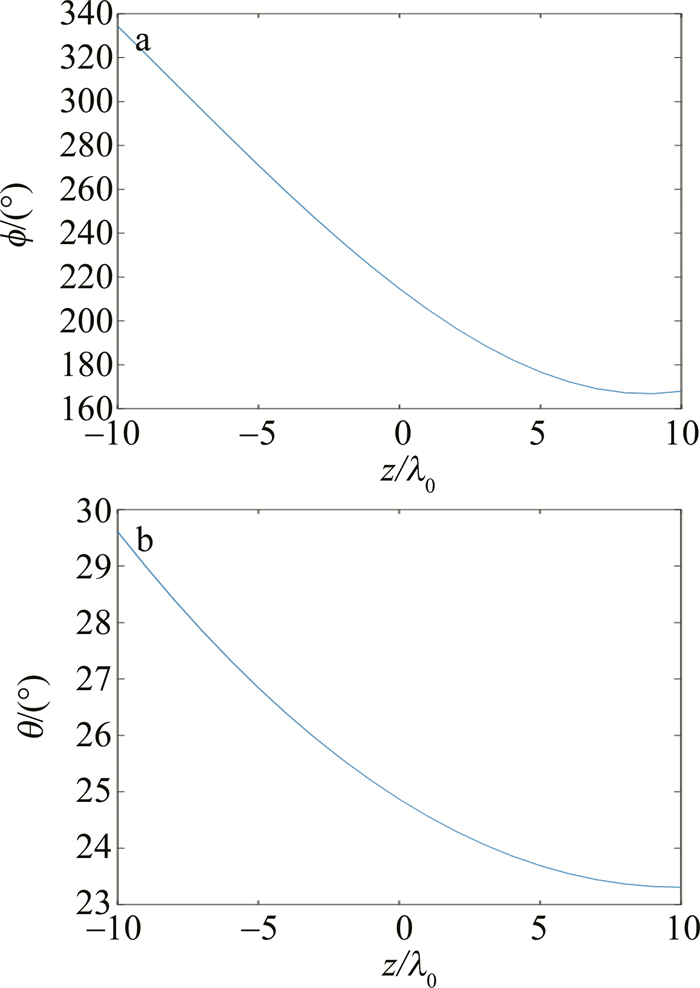
通过数值模拟,得到了空间角辐射达到最大值时方位角θ和ϕ的值,如图 4所示。

Figure 4. When the electron initial position of the electron changes in the interval [-10λ0, 10λ0] and the space angular radiation reaches the maximum, the change trend of azimuth θ and ϕ value
仿真所得数据与理论计算值完全相同,因此可知,随着电子初始位置的右移,空间角辐射达到最大值时,极角θ和方位角ϕ的值有不断减小的趋势,且任意时刻的空间角辐射都集中在一个小圆锥体中。这表明具有最大空间辐射能量的一支逐渐靠近z轴,并且在z0=5λ0后趋于稳定,(θ, ϕ)=(23.5°, 175.5°)。
-
本文中探究了不同初始位置情况下,圆偏振激光脉冲中高能电子运动轨迹和空间角辐射的变化规律。结果表明,高能电子在圆偏振紧聚焦激光脉冲中的运动呈螺旋状,且随着初始位置沿+z轴方向增大,后部分运动轨迹呈现出越来越明显的稀疏圆状,且随着电子初始位置沿+z轴方向增大,空间角辐射达到最大值时所对应的方位角不断减小。这些结论为进一步深入探究电子初始位置对圆偏振激光脉冲中高能电子空间辐射特性的影响奠定了基础。

 Map
Map





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: