HTML
-
焊接缺陷是破坏工件工作稳定性的重要因素之一[1-2]。焊接过程中,由于各种因素的干扰,易造成焊接的不稳定状况,从而产生裂纹、凹坑和未熔合等缺陷[3-4]。磁光成像作为一种新型的缺陷无损检测技术,能够实现对焊接缺陷的在线检测,并使焊接缺陷可视化,具有良好的检测能力,是一种绿色、环保、直观、高效的无损检测技术[5]。
磁光图像是对焊接缺陷的客观展示,其图像质量对肉眼观测及模式识别有着直接的影响,故而对磁光图像进行处理十分必要。目前,在磁光图像去噪方面,空域上常用高斯滤波、自适应中值滤波等,频域上常用高斯低通滤波,对低频的焊接缺陷信息进行保留,过滤高频的噪声信息[6-7]。在图像增强方面,针对于磁光图像灰度集中的问题,运用灰度直方图均衡化扩充磁光图像的灰度区间,增强图像对比度[7];或对不同角度下、旋转磁场下或组合磁场下同一缺陷的不同图像进行图像融合,既解决了磁光图像只能显示单一方向信息的缺点,也增强了缺陷部分的对比度[8]。在轮廓提取方面,采用Otsu法获取图像最佳阈值,后进行阈值分割,再通过Canny等算子提取缺陷轮廓信息[6]。
-
焊接缺陷磁光成像检测基于缺陷漏磁场原理及法拉第磁致旋光效应,如图 1所示。
励磁装置在通入直流/交流电时,线圈中会产生恒定/交变的磁场,磁场磁化磁芯,向空间中辐射磁场。使试件中产生横向流动的磁场,当磁场接触缺陷时,会在缺陷分界面上发生折射,使试件内部的磁场扩散到空气中,形成缺陷处的漏磁场。漏磁场进入磁光传感器的磁光薄膜中,与经过偏振片及凸透镜的线偏振光在磁光薄膜中接触,发生磁致旋光效应,使线偏振光发生偏转,最后经反射、凸透镜及检偏器被互补金属氧化物半导体(complementary metal oxide semiconductor, CMOS)相机捕捉,形成包含缺陷漏磁场信息的磁光图像。偏转角度ϕ可由下式计算得出[9]:
式中, ϕ为线性偏振光在磁光薄膜中的偏转角度;V为费尔德常数;L为线性偏振光在磁光薄膜中经过的路程;B为磁光薄膜中的磁感应强度。
-
采用激光点焊对200 mm×100 mm×1.5 mm的65Mn钢板进行搭接焊[10],激光功率1 kW~1.5 kW,焊接时间1 s~2 s,离焦量0 mm,氩气流量20 L/min。焊接缺陷磁光成像检测系统主要包括磁光传感器、直流/交流电源、励磁装置、三轴运动平台、工控机及图像采集设备等,如图 2所示。图中, DC/AC(direction current/alternating current)是直流/交流电源, IPC(industrial personal computer)为工控机。
1.1. 磁光成像检测原理
1.2. 磁光成像检测系统
-
采用直流励磁方式获取激光点焊裂纹磁光图像,采样频率为75 frame/s,图像尺寸为400 pixel×400 pixel。选取其中一组为示例,缺陷部分显微图像及磁光图像如图 3a及图 3b所示。
仿真参数如表 1所示。通过有限元分析模拟形状相似的裂纹缺陷,仿真模型如图 4所示。
current/A coil turns per coil magnetic core test sample specimen size/mm defect location defect depth/mm 1 copper 350×2 Mn-Zn 65Mn 200×100×1.5 right under plate 0.4 Table 1. Simulation parameters of welding defects
焊接缺陷磁光图像是对缺陷处漏磁场的反应,提取仿真缺陷中心磁场曲线及磁光图像第200列灰度曲线如图 5a及图 5b所示。图 5a纵坐标为磁场z分量。磁光图像曲线整体变化趋势与仿真磁场曲线一致,由于仿真缺陷尺寸与实际缺陷尺寸间存在差异,变化幅度存在一定的差别。两曲线中一高一低的极值点表示缺陷的轮廓点。仿真磁场曲线两极值间横坐标对应缺陷的实际宽度,但磁光图像由于传感器本身具有一定的提离值,所表现出的宽度信息要比实际缺陷宽度大。
磁光图像灰度具有连续性和集中性。磁光图像在缺陷区域的灰度幅值变化并不大,且在幅值两侧受磁场的扩散影响,两侧灰度也会有相应的提高,使缺陷轮廓难以捕捉。磁光图像整体灰度较为集中,提取其灰度直方图,如图 6所示。整体的像素值集中在50~200列区间内,造成磁光图像缺陷区域与背景区域灰度差值不大,图像对比度低,往往需要对图像进行增强。
对比图 5a与图 5b可以看到,磁光图像中分布着大量的噪点,呈上下波动趋势。这种噪点不仅出现在直流励磁下的磁光图像中,在交变、旋转等励磁中也有出现。为了解磁光图像中噪声的类型,并考虑单一图像的偶然性,选取裂纹及无缺陷磁光图像,分别如图 7a及图 7d所示。提取裂纹图像第200列灰度曲线及列平均灰度曲线,如图 7b及图 7c所示,提取无缺陷图像第200行灰度曲线及行平均灰度曲线,如图 7e及图 7f所示。可以清晰地看到经过均值处理后的曲线上噪声减少了很多,且噪声的变化幅度大大减小,曲线更贴近于仿真磁场曲线。由于磁光图像噪声是始终存在的,并不因为有无缺陷而影响噪声的存在,且噪声受均值影响大,这些特性都符合加性噪声的特征[11]。
-
针对于焊接缺陷磁光图像的加性噪声特性,选用快速非局部均值(fast non-local mean, FNLM)滤波对磁光图像进行去噪。与传统的均值滤波不同,FNLM将局部区域均值扩展为非局部区域均值,在处理窗口内的目标点像素值是由于其具有相同邻域结构的像素点加权平均得到,并利用积分图对非局部均值滤波(non-local mean, NLM)算法进行加速。在尽可能地保留图像纹理及边缘等细节的同时,完成对图像的去噪。NLM示意图如图 8所示。
其滤波过程如下[12]:
式中, x为当前滤波点;Ω为整幅图像区域;y为x的处理窗口Ωx中的像素点;u(x)为去噪后的图像,v(y)为原始图像;ω(x, y)是权重值,表示在原始图像v(y)中,目标像素x和像素y的相似度,且ω(x, y)>0,∑ω(x, y)=0。
考虑图像中噪声的影响,单一像素之间相似度并不可靠,故将像素之间的相似度以像素邻域之间相似度代替,邻域间的相似度高即表明邻域中心点像素的相似度高。邻域间高斯加权的欧氏距离计算公式如下[12]:
式中, z(x)为归一化因子,是所有ω(x, y)的和;h>0是滤波系数,h越大,平滑效果越强;v(x)和v(y)表示像素x和像素y的邻域,该邻域一般要小于搜索区域Ωx; ‖v(x)-v(y)‖2, a2表示两个邻域的高斯加权欧氏距离,a>0,为高斯权重值,即对应正态分布的值,表示邻域之间随距离增加,其权重会越来越小,且权重服从正态分布。
在NLM滤波的基础上,FNLM引入积分图思想改变运算方式,并以欧氏距离代替高斯加权的欧氏距离,大大减小了图像邻域之间欧氏距离的计算数量[13]。使用NLM滤波处理400 pixel×400 pixel磁光图像所用时间为27.363562 s,使用FNLM滤波处理所用的时间为0.363899 s。
原始磁光图像如图 9a所示, 经过FNLM处理后的磁光图像,噪声数量大大减少,图像的缺陷信息得到了较好的保留,如图 9b所示。分别提取两图像第200列灰度曲线, 如图 9c及图 9d所示。经过去噪后的曲线其整体变化趋势没有改变,且曲线更贴近于仿真曲线的趋势,突变的噪声基本清除,整体图像质量提高。

Figure 9. Comparison between the original magneto-optical image and the magneto-optical image after FNLM processing
与目前磁光图像常用滤波器进行对比, 如图 10所示。经FNLM滤波后的磁光图像,噪点更少,且缺陷信息得到了保留。磁光图像的去噪过程是曲线离散变平滑的过程。图 10中几种滤波在磁光图像去噪上的性能指标如表 2所示,其中针对于磁光图像标准差及熵值越小,表示图像平滑效果越好。
originalimage adaptive median filtering Gaussianfiltering meanfiltering FNLM standard deviation S 30.2035 30.1652 30.0985 30.0985 30.0465 entropy E 6.7714 6.7633 6.7488 6.7398 6.0395 Table 2. Performance indexes of several filters in magneto-optical image denoising
选用标准差S及熵E作为磁光图像去噪的性能指标,标准差表示了图像的离散程度,如下式所示[14]:
式中, F(i, j)为输入图像;u为图像均值;M,N分别为图像行列像素个数;i,j分别为图像像素横纵坐标。
图像熵表示了图像信息的混乱程度,如下式所示[15]:
式中, Pij为单个灰度出现的概率;f(i, j)表示像素点出现的频次; W为图像尺寸大小。
-
由于磁光图像灰度的连续性,灰度变化较为缓慢,且缺陷信息在一高一低两极值之间,难以通过单一阈值对图像灰度进行阈值分割。基于磁光图像缺陷信息区域与两侧背景区域梯度值相异的特性,本文中采用Sobel算子,将磁光图像灰度图像转化为1阶梯度图,对梯度图进行阈值分割,提取去噪后的磁光图像1阶梯度图,如图 11a所示。经过FNLM滤波去噪后的图像,在像素点灰度邻域内会出现灰度值一致的情况,导致梯度图缺陷信息中出现梯度0点,出现缺陷信息离散的情况,采用Savitzky-Golay滤波器对图像进行线性平滑[16],补全后的1阶梯度图如图 11b所示。图像整体性更好,且对梯度图像中的背景信息进行削弱,便于后续的阈值分割处理。
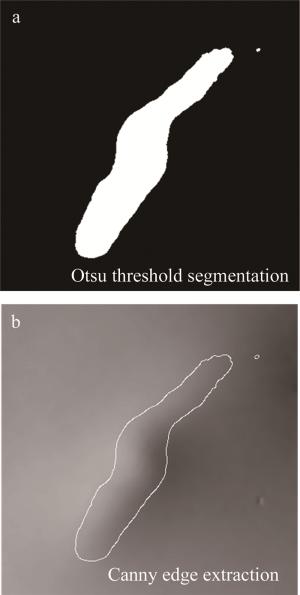
平滑后的缺陷磁光图像,缺陷信息已较为清晰,选用Otsu法,获取使背景与缺陷区域类间方差最大的最优阈值,并对缺陷梯度图像进行阈值分割,分割后的图像如图 12a所示。使用Canny边缘提取算子对阈值分割后的图像进行边缘提取,并将阈值边缘叠加到FNLM去噪后的图像,如图 12b所示。
针对激光点焊缺陷的随机性,并为证明本文作者所提出的图像处理流程的效果及适用性,选取4幅磁光图像,对其用本文中的流程进行处理,其结果如图 13所示。
3.1. 基于快速非局部均值滤波的去噪
3.2. 基于Sobel算子磁光图像梯度图的阈值分割及边缘轮廓提取
-
通过研究激光点焊缺陷的磁光图像特征,并与有限元模拟仿真结果对比,分析磁光图像灰度的连续性、集中性及加性噪声类别。针对焊接缺陷磁光图像轮廓难以提取的问题,提出一种磁光图像去噪及轮廓提取的处理方法。利用FNLM对磁光图像进行去噪,并与传统滤波器进行对比分析。结果表明, 经FNLM处理后的磁光图像,减小了灰度曲线的离散性,使其更贴近仿真磁场曲线。利用磁光图像缺陷信息与背景信息梯度值相异的特性,在磁光图像1阶梯度图的基础上进行Otsu法阈值分割与边缘检测,并对多幅激光点焊裂纹磁光图像使用该方法进行处理。可知该方法在有效去除噪声的基础上,能较好地提取缺陷轮廓信息。

 Map
Map















 DownLoad:
DownLoad:











